Fig. 1.
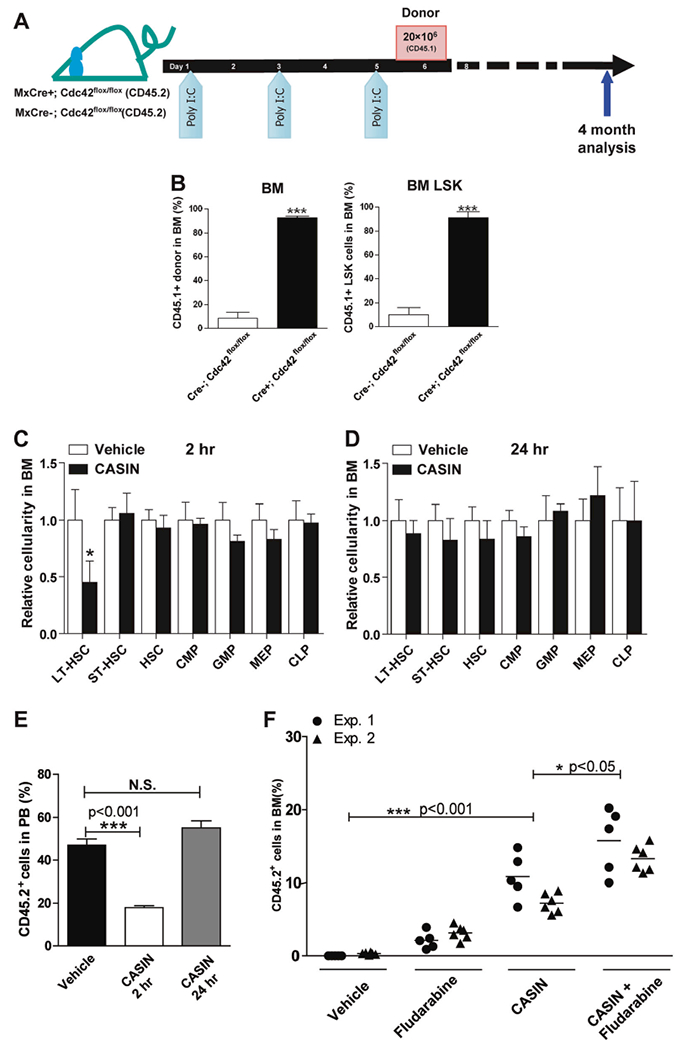
Cdc42 targeting opens BM niche. a, b A single dose of donor BM cell infusion effectively engrafts recipient mice upon deletion of Cdc42 in host BM. Recipient mice (Mx:Cre−/−; Cdc42flox/flox v.s. Mx: Cre+/+; Cdc42flox/flox) were injected with Poly I:C three times 1 day apart and transplanted with 2 × 107 congenic BM cells (CD45.1+) 1 day after the last injection a. Percentage of donor-derived chimerism (CD45.2+) in total BM cells (left panel) and LSK BM cells (right panel) of CASIN-treated BoyJ recipients (CD45.1+) v.s. vehicle 4 months after transplantation b. Results are means plus or minus SD from three independent experiments (n = 6 for each experimental group). *** p < 0.001. c–e CASIN administration phenocopies the effect of Cdc42 gene targeting in host mice to facilitate donor HSC engraftment. Relative changes in the number of phenotypic long term (LT)-HSC (Lin−IL-7R−Sca1+c-kit+CD34−) and various progenitor subpopulations were measured in CASIN- or vehicle-treated mouse BM (1.2 mg/kg, IV) at 2 h c or 24 h d. Results are representative of three independent experiments (n = 4). * p < 0.05. The BM cells harvested from these donor mice (3 × 106) were competitively transplanted into BoyJ recipients (CD45.1+) at a 1:1 ratio with CD45.1+ BM cells, and the chimera were analyzed 10 months after the competitive transplantation e. Results are representative of three independent experiments (n = 8 for each recipient group). *** p < 0.001. f CASIN promotes LT-HSC engraftment and synergizes with Fludarabine in a non-myeloablative conditioning regimen. Two separate cohorts of syngeneic BoyJ recipient mice were conditioned with vehicle, CASIN (twice at 1.2 mg/Kg), Fludarabine (three times at 75 mg/kg, IP), or CASIN together with Fludarabine prior to transplantation with congenic CD45.2+ BM cells (5 × 106). Percentages of donor-derived mononuclear cells in the PB of the recipients were measured 4 months after transplantation. * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001
