Fig. 2.
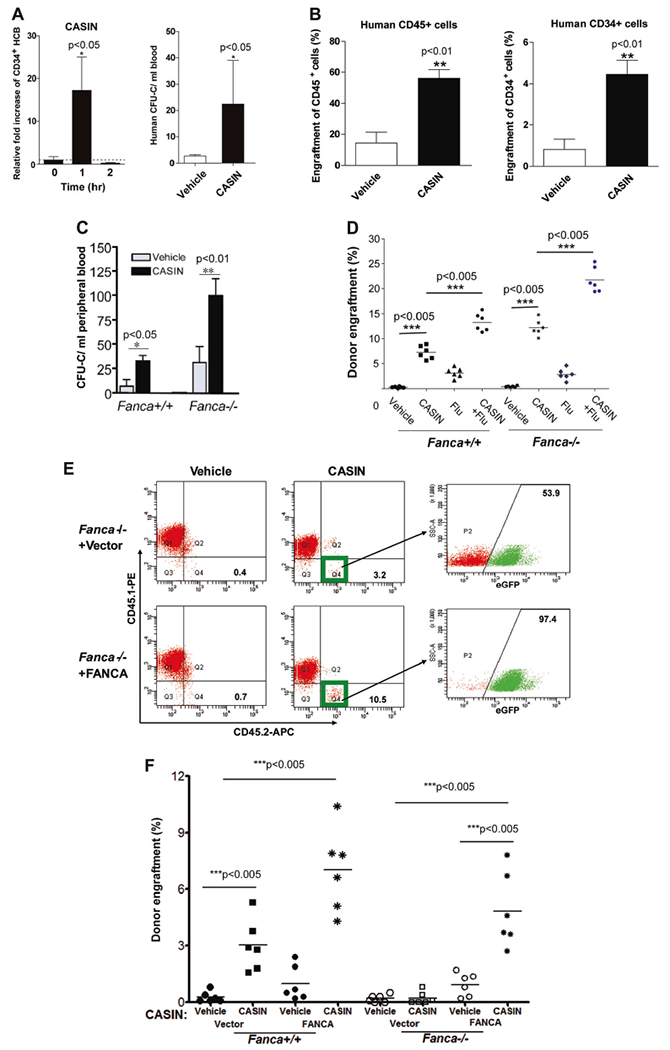
CASIN application to human cord blood and FA transplantation. a CASIN mobilizes CD34+ HCB cells in xenografted NSG mice. CD34+ HCB cells were transplanted into sublethally irradiated NSG recipient mice. Four month later, xenografted mice were treated with CASIN (1.2 mg/kg, iv). Peripheral blood (PB) were then obtained at the indicated time points and subjected to Flow Cytometry analysis for hCD34. Relative fold increase of CD34+ HCB chimerism (left) plus or minus SD (n = 13 in CASIN groups and n = 10 in control group) and CFU-C numbers in PB of mice (right) are shown. n = 5 in CASIN group and four in vehicle group. * p < 0.05. b CASIN enhances engraftment of CD34+ HCB cells in immunodeficient NSG mice without myeloablation. Recipient NSG mice were conditioned with vehicle or CASIN (1.2 mg/kg) 24 and 2 h prior to BM transplantation and then transplanted with 2 × 105 CD34+ HCB cells by intrafemoral injection. Percentages of donor-derived human CD45+ in PB (left) or CD34+ in BM (right) were assessed by Flow Cytometry 4 months after transplantation. n = 5 per group. ** p < 0.01. c CASIN further increased spontaneous mobilization of Fanca−/− BM progenitors. WT or Fanca−/− mice were injected with CASIN (1.2 mg/kg, IP) or Vehicle, and 48 h later, PB from the treated mice were subjected to progenitor assay for CFU-C activity. Results are means plus or minus SD from three independent experiments (n = 9 per group). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01. d CASIN synergizes with Fludarabine (Flu) on HSC engraftment. Fanca+/+ and Fanca−/− recipients were conditioned with CASIN (1.2 mg/kg, IP, 24 and 2 h prior to BMT), Fludarabine (75 mg/kg, i.p. administration, 72, 48, and 24 h prior to BMT) or CASIN plus Flu in parallel with vehicle controls, and then transplanted with congenic BM cells (5 × 106 cells/mouse). Percentages of donor-derived cells in BM of recipients were determined by Flow Cytometry analysis. Results are representative of three independent experiments (n = 6 per group). *** p < 0.005. e CASIN promotes engraftment of gene-corrected Fanca−/− HSCs in wild-type recipients. BoyJ recipients were pre-conditioned with vehicle or CASIN (twice at 1.2 mg/kg), and transplanted with 2 × 105 Fanca−/− Lin− BM cells transduced with retrovirus expressing eGFP only (Vector) or FANCA. Four months later, PB cells from the transplanted mice were stained with antibodies against CD45.1 and CD45.2, and donor-derived CD45.2+ cells were gated and analyzed by flow cytometry for GFP-positive and GFP-negative cell populations. Note that > 90% of donor-derived cells in the CASIN group are gene-corrected (eGFP-positive) cells. f CASIN promotes engraftment of gene-corrected Fanca−/− HSCs in Fanca−/− recipients. Similar donor cells and conditioning regimens as in e were used except that the transplant recipients were either Fanca+/+ or Fanca−/− mice. Donor engraftments were assayed by FACS analysis of eGFP+ cells in the recipient BM 4 months posttransplant. Results are representative of three independent experiments (n = 6 per group). *** p < 0.005
