Figure 1.
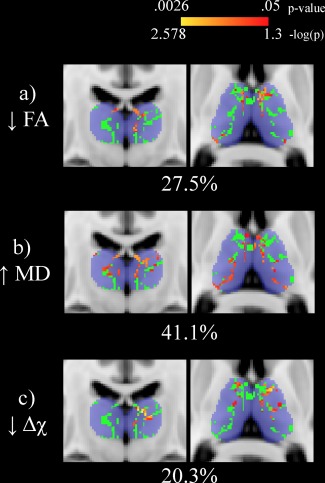
Univariate voxel‐wise analysis of the thalamic white matter skeleton (shown in green) comparing healthy controls (HCs) and multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. Significant differences (p < .05) are shown in red‐yellow with p values having been log transformed for improved visibility. Warmer colors are indicative of smaller p values. Decreased fractional anisotropy, increased mean diffusivity, and decreased susceptibility are seen in MS patients compared to HCs. Percentages refer to the proportion of significantly different voxels between MS patients and HCs in the thalamic skeleton. The Harvard‐Oxford thalamic ROI is shown for reference in transparent blue. The slice shown corresponds to standard space MNI coordinates of Y = −17, Z = 8. Abbreviations: FA: fractional anisotropy; MD = mean diffusivity; Δχ = magnetic susceptibility; HC = healthy control; MS = multiple sclerosis [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
