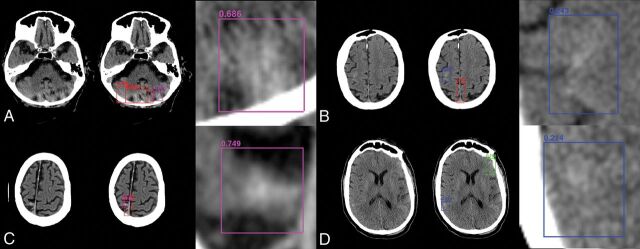
Fig 4.
Sample network predictions: false-positives and false-negatives. Network predictions by the algorithm include bounding-box region proposals for potential areas of abnormality (to focus algorithm attention) and final network predictions including confidence of results. False-positive predictions for hemorrhage (purple) often include areas of motion artifacts and/or posterior fossa beam-hardening (A) or high-density mimics such as cortical calcification (C). False-negative predictions for excluded hemorrhage often include small volume abnormalities with relatively lower density, resulting in decreased conspicuity. Examples include subtle subarachnoid hemorrhage along the posterior right frontal lobe (B) and right inferior parietal lobe (D).