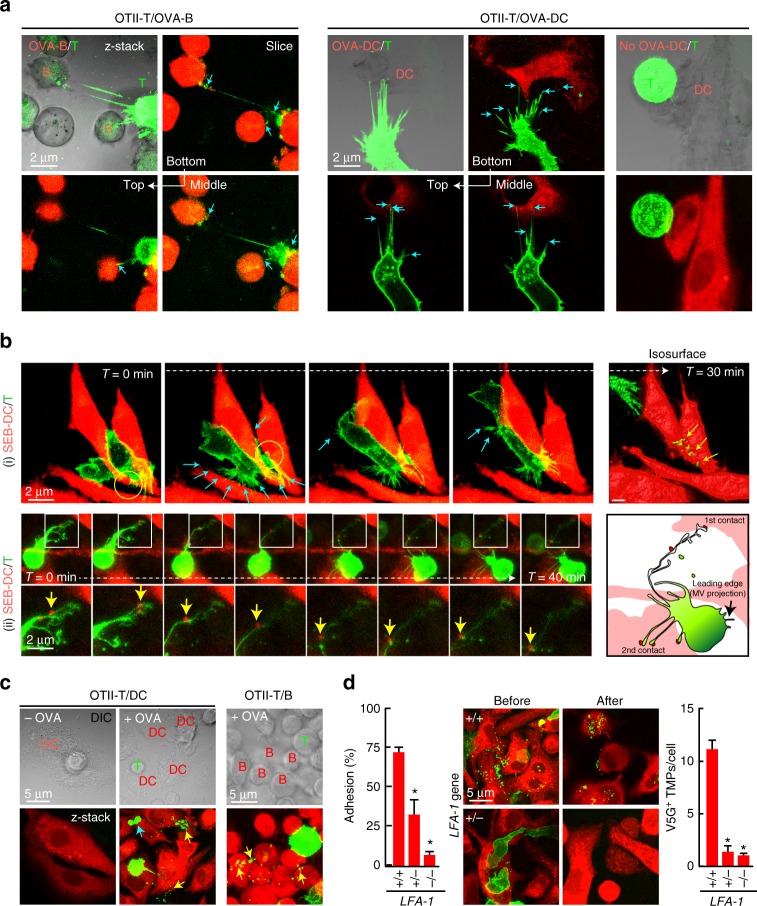
Fig. 4.
T cells leave TMPs on the surface of APCs in an integrin LFA-1-dependent manner. a Confocal microscopy of V5G+ OTII CD4+ T cells incubated with OVA323–339-loaded B cells or DCs for 30 min. Arrows indicate multiple contact sites. b Time-lapse imaging of V5G+-TMP generation from mouse T cells. CD4+ T cells were retrovirally transduced with V5G and incubated with SEB-loaded DCs for 30 min. Cyan arrows indicate the multiple contact sites. V5G+ TMPs (yellow arrows) on DCs in the last panel were visualized by isosurface rendering using Imaris software (see also Supplementary Movies 5 and 6). c V5G+ OTII CD4+ T cells from a were incubated for 1 h and observed by confocal microscopy. V5G+ TMPs are indicated by yellow arrows. d Adhesion of CD4+ T cells from wild type, LFA-1+/−, and LFA-1−/− mice to mICAM-1-Fc-coated plates after anti-CD3/28 stimulation. Data represent the mean of three experiments ± SEM (left). Mouse CD4+ T cells from wild type, LFA-1+/−, and LFA-1−/− mice were retrovirally transduced with V5G, incubated as described in a, and observed by confocal microscopy. The number of V5G+ TMPs per DC was quantified using Imaris software. Data represent the mean of three experiments ± SEM. *P < 0.01 vs. wild-type T cells