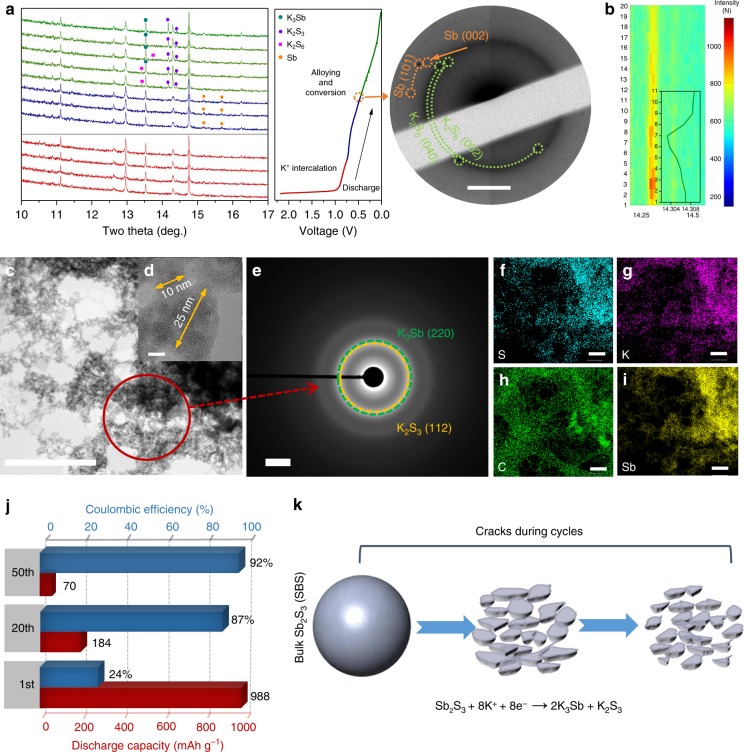
Fig. 1.
Investigation of the electrochemical mechanism of bulk Sb2S3 (SBS) anode and the failure mechanism. a In situ synchrotron XRD patterns of Sb2S3 electrodes upon K insertion at various potentials (left) and ex situ SAED pattern (right) (discharged to 0.5 V) with high-resolution image revealing weak reflections. b Image plots of the in situ XRD diffraction patterns of the (212) reflection of Sb2S3 during the intercalation stage and corresponding fitted peak (inset), indicating the peak shift. c, d TEM images of the first discharge product and high-resolution TEM image of the bulk Sb2S3 after potassiation. e SAED pattern of indicated area in (c). f–i STEM images with elemental mapping of sulfur, potassium, carbon, and antimony. j Discharge capacity and columbic efficiency of bulk Sb2S3 at different cycles. k Schematic illustration of pulverization of Sb2S3 during charge/discharge. Scale bars: 2 nm−1 (a); 0.5 µm (c); 5 nm (d); 2 nm−1 (e); 250 nm (f–i)