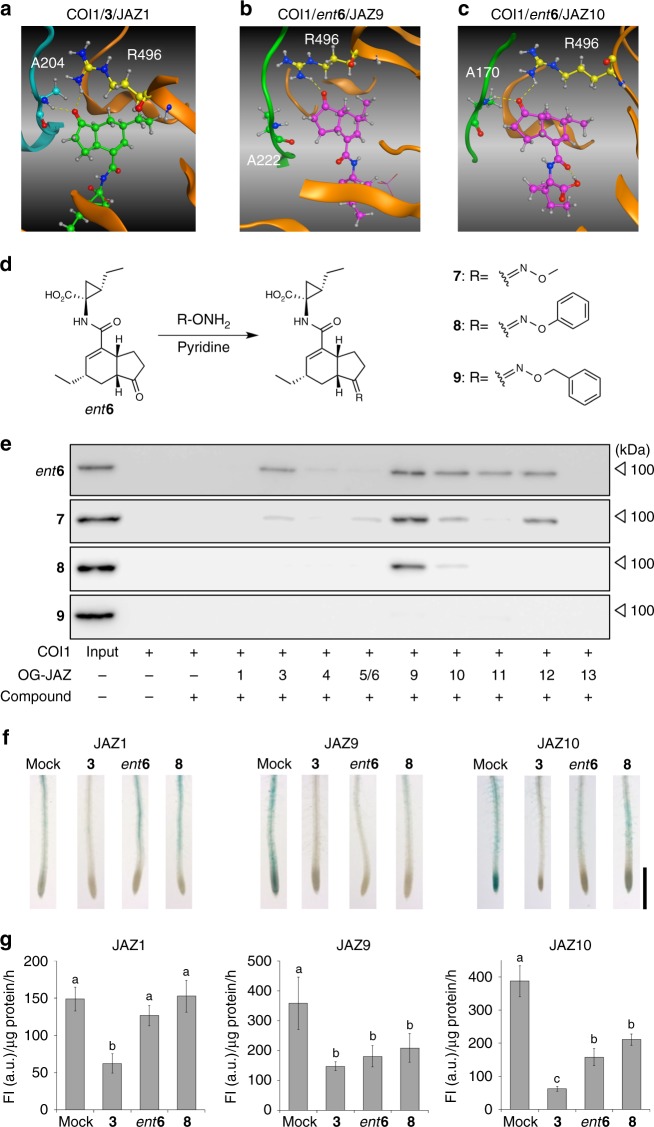
Fig. 3.
Rational design of JAZ subtype-selective agonist by an in silico docking study. a The obtained average structure of MD simulation of COI1-3-JAZ1. The hydrogen bond between the ketone group of 3 with A204JAZ1 or R496COI1 is indicated by a yellow dotted line. b The obtained average structure of COI1/JAZ9 complexed with ent6, which was constructed by in silico docking analyses and MD simulation. The hydrogen bond between the ketone group of ent6 with R496COI1 is shown as yellow dotted line. c The obtained average structure of COI1/JAZ10 complexed with ent6, which was constructed by in silico docking analyses and MD simulation. The hydrogen bond between the ketone group of ent6 with A170JAZ10 (corresponding to A204JAZ1) or R496COI1 is indicated by a yellow dotted line. d Synthesis scheme for compounds 7–9 from ent6 as a starting material and corresponding oxime molecules. e Pull-down assay of purified GST-COI1 (5 nM) with all OG-conjugated JAZ peptides (10 nM) in the presence of ent6, 7, 8, or 9 (500 nM). HRP-conjugated anti-GST antibody was used to detect GST-COI1. f Evaluation of GUS activity in the roots of 4-day-old 35S:JAZ1-GUS, 35S:JAZ9-GUS, and 35S:JAZ10-GUS plants. Seedlings were pretreated for 30 min with or without ligand (3, ent6, or 8, 1 µM), and stained with 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl glucuronide; the experiments were repeated three times with similar results. Scale bar, 1 mm. g Quantification of GUS activity in 20 roots of 4-d-old 35S:JAZ1-GUS, 35S:JAZ9-GUS, and 35S:JAZ10-GUS plants (n = 4). Significant differences were evaluated by one-way ANOVA/Tukey HSD post hoc test (p < 0.01). Seedlings were pretreated as described above. Three independent replicates were measured, and values represent mean ± s.d. (Supplementary Methods)