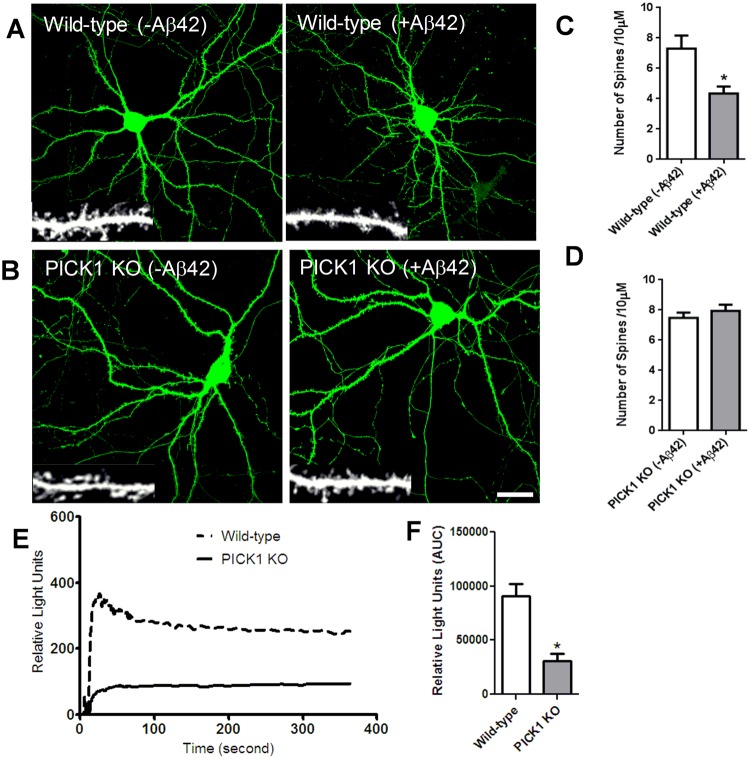
Figure 1.
PICK1 deletion attenuates Aβ-induced modulation in dendritic spine density and intracellular calcium concentration. (A,C) Soluble oligomeric Aβ42 reduces dendritic spine density. (A) Cultured mouse hippocampal neurons expressing GFP to visualize neuron morphology were treated with Aβ42 (5 μM). Individual dendritic segments are shown as insets in grayscale for control (non-treated) and Aβ42-treated neurons. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Histograms show quantification of spines per 10 μm of dendrite length. n = 13 neurons for each group (*P < 0.05). (B,D) PICK1 deletion prevents Aβ42-induced decrease in dendritic spine density. Hippocampal neurons cultured from wild-type (A) and PICK1 knockout (KO) (B) mice were transfected with GFP to outline neuron morphology, and were either untreated or treated with Aβ42. Individual dendritic segments are shown as insets in gray scale for wild-type and PICK1 KO neurons. Scale bar, 8 μm. (D) Histograms show analysis of spines per 10 µm dendrite length in PICK1 KO mice neurons. n = 13 neurons for each group.(E,F) PICK1 attenuation decreases intracellular calcium concentration. (E) AMPA receptor- dependent calcium influx was measured in hippocampal neurons cultured from wild-type and PICK1 knockout (PICK1 KO) mice. (F) Quantification of intracellular calcium concentration in wild-type and PICK1 KO mice hippocampal neurons (*P < 0.05).