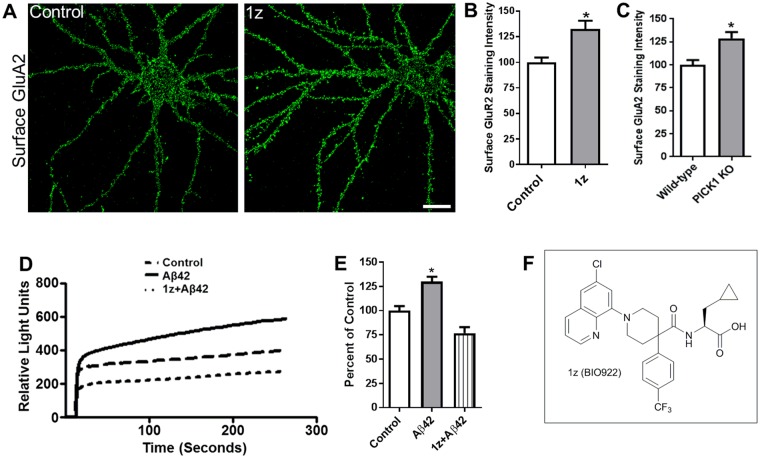
Figure 5.
PICK1 inhibition stabilizes surface GluA2 and attenuates Aβ-mediated increase in intracellular calcium concentration. (A–C) PICK1 inhibitor stabilizes surface AMPA receptors. (A) Cultured hippocampal neurons were untreated (left) or treated with the PICK1 inhibitor 1z (BIO922, 3 μM) (right) for 24 hours, and immunostained for surface GluA2. Scale bar, 20 μm (B), Histograms show quantification of surface GluA2 immunofluorescence intensity normalized to control (non-treated) values. n = 15 control, n = 15 (1z, BIO922) treated (P < 0.005). (C) Histograms show quantification of staining intensities of surface GluA2 in wild-type and PICK1 KO mice neurons normalized to the wild-type group n = 16 wild-type, n = 18 PICK1 KO (*P < 0.05). (D,E) PICK1 inhibitor blocks Aβ42-induced increase in intracellular calcium concentration. (D) AMPA receptor-dependent calcium influx was measured in cultured hippocampal neurons left untreated (control), or treated with Aβ42 in the absence (Aβ42) or presence of PICK1 inhibitor (Aβ42 + 1z, BIO922). (E) Histograms show quantification of intracellular calcium concentration normalized to control (non-treated) values comparing Aβ42-treated with Aβ42 + 1z-treated cells (*P < 0.05). (F) Structure of compound 1z, BIO922.