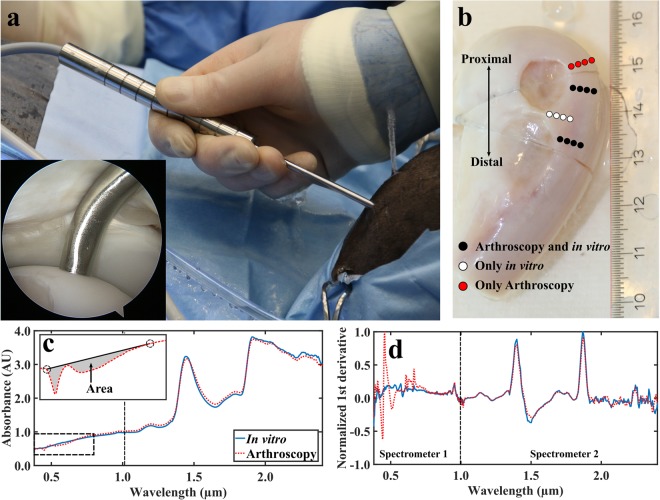
Figure 1.
The novel fibre optic probe in an equine knee joint in vivo (a) with the probe tip in contact with cartilage surface (inset). Locations of NIRS measurements conducted in vivo during arthroscopy and in vitro in the laboratory (b). Comparison of average smoothed (c) and first derivative pre-processed (d, not used for modelling) spectra collected in vivo and in vitro with two separate spectrometers to cover the wide spectral region. NIRS measurement locations indicated with white and black dots were subjected to biomechanical and micro-CT reference measurements (b). For the red dots, values of reference parameters were only predicted based on ANN models. In subfigure (c), calculation of area between a two-point linear fit and measured spectrum was applied to detect outlier spectra. In subfigure (d), the 1st derivative spectra (not used for analysis) highlight the contribution of light from the conventional arthroscope at the spectral region of 0.42–0.75 µm.