Figure 1.
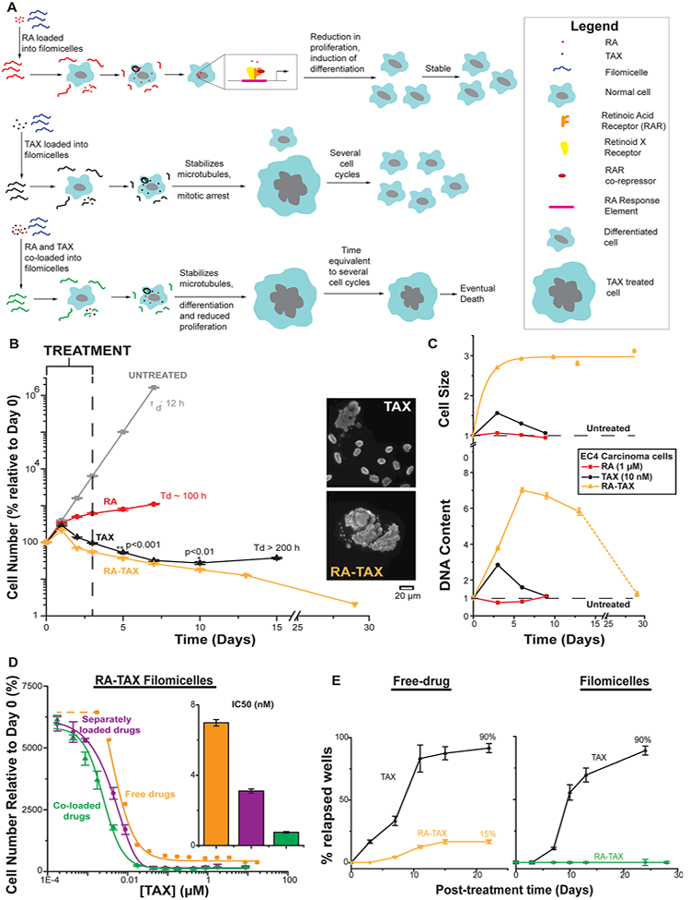
(A) Schematic depicting effect of RA, TAX, and RA-TAX on cells after filomicelles release drugs. Only RA-TAX combination leads to durable effects. (B) Cells treated with RA consistently increase in number, consistent with RA not killing cells, just differentiating them. TAX treated cells decline in number initially (similar to initial tumor shrinkage), but cell death plateaus after a week when proliferating cell numbers overtake dying ones. RA and TAX treated cells, on the other hand, consistently decrease in number, indicating a more durable treatment. (C) Quantification of DNA content and cell size after drug treatment. DNA content increases for TAX and RA-TAX due to incomplete cell division; it decreases for RA due to a lower number of proliferating cells (and hence lower DNA replication before division). DNA content for cells treated with single drugs returns to normal after about 6 days (about 3 days after treatment), indicating the transient nature of single drugs, whereas DNA content for RA-TAX decreases much more slowly. Similarly, cell size for single drugs returns to normal within 3 days, indicating the transient nature of single drugs. However, they remain consistently high for combination treatment. (D) Delivery systems with two payloads can be coloaded onto the same micelle or on separate filomicelles which are then mixed. At high concentrations, both are equally effective. However, at therapeutic concentrations (around IC50), coloaded filomicelles are 4 times more potent than separately loaded filomicelles (inset bar graph). (E) Most wells treated with TAX relapse (92%), the rate is much lower for RA-TAX treated wells (15%) 22 days post-treatment, indicating that 85% of wells exposed to RA-TAX die, which illustrates a much more durable treatment than the single drug. Loading TAX onto filomicelles does not alter relapse (89% of TAX treated wells experienced relapse), highlighting again the limitation of a single drug. The efficacy of RA-TAX was greatly improved via loading onto filomicelles, with no relapses in cells observed after 30 days.
