Figure 6.
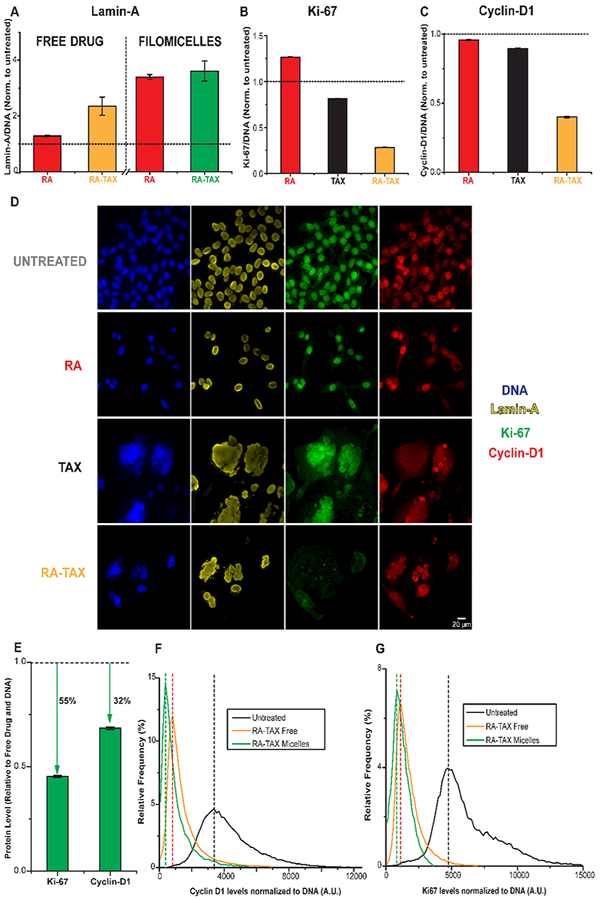
(A) RA and TAX treated cells were found to have higher levels of lamin-A than untreated ones, suggesting differentiation. Lamin-A levels were higher for drugs delivered via nanocarriers than for free drugs. (B,C) RA-TAX treated cells have lower levels of and Cyclin-D1 than TAX or RA alone treated cells. The durability of RA-TAX combination might be explained by its inhibitory role on protein synthesis (via Ki-67) rather than regulation of cell cycle (CyclinD1). (D) Images (40× magnification) of cells treated with RA, TAX, and RA-TAX combination, as well as untreated. All groups except RA-TAX stain positive for Ki-67. Lamin-A is higher in RA-TAX treated cells. (E) Delivery of drugs via filomicelles has been proven to be superior to free drugs, and this mode further reduces levels of these two proteins, with Ki-67 levels being halved compared to free drug treated. (F,G) histogram of Ki-67 and Cyclin D1 levels after treatment with various drugs loaded onto filomicelles. The fractions of cells null for these proteins progressively increases from no treatment to free drug to micellar drug delivery.
