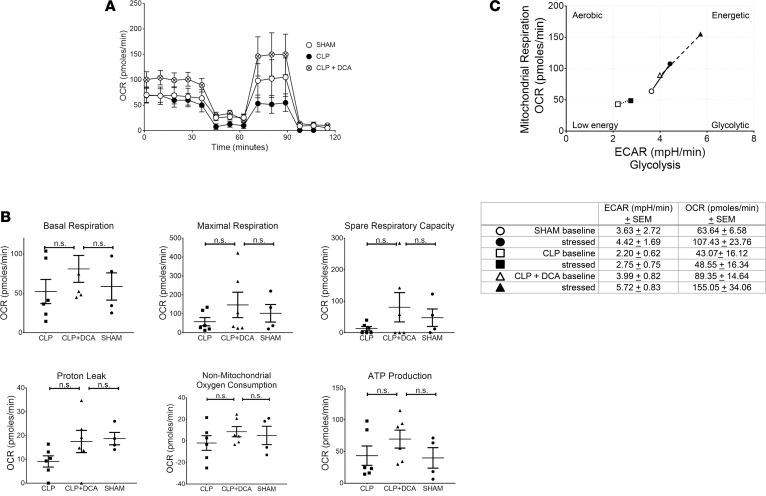
Figure 3. Dichloroacetate (DCA) treatment increases mitochondrial respiration and improves the metabolic potential of mitochondria in splenocytes from septic mice.
Seahorse XF24 Analyzer and the mitochondrial stress test was used to determine oxygen consumption rate (OCR) in splenocytes from SHAM (n = 4), cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) (n = 6), or CLP+ DCA (n = 6) mice. A shows tracing of average values from SHAM, CLP, and CLP+ DCA groups. (B) OCR data generated using the mitochondrial stress test by Seahorse WAVE 2.4 Software (Agilent) was analyzed using GraphPad Prism 7.04 Software and ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD post-test. (C) The Seahorse WAVE 2.4 Software was used to evaluate the metabolic potential of mitochondria using the extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) and OCR in splenocytes from SHAM (n = 4), CLP (n = 6), and DCA-treated CLP mice (n = 6) as measured by the Seahorse XFe24 Analyzer.