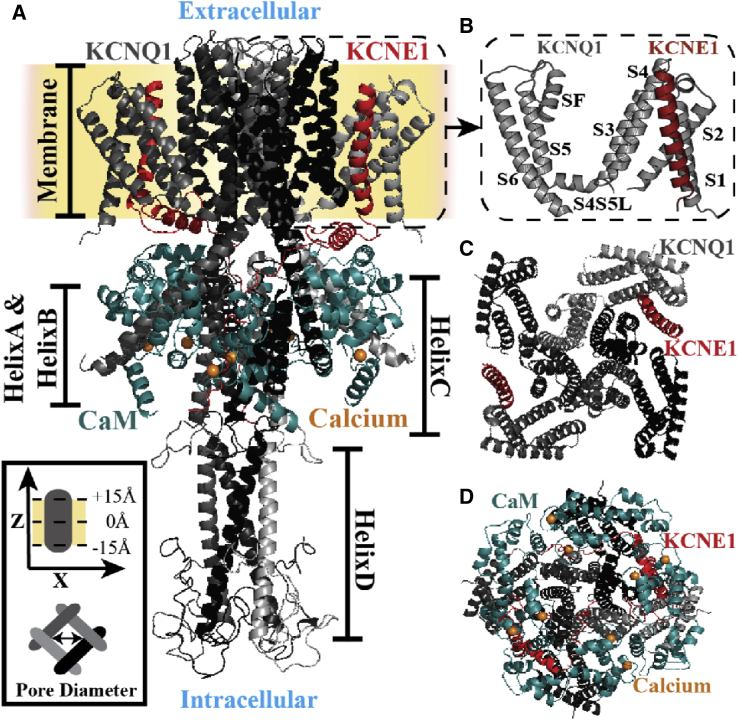
Figure 1.
IKs structure. (A) A side view of initial IKs structure (KCNQ1 tetramer bound to two KCNE1) is shown. CaM is bound to HelixA&B and is proximal to the KCNE1 cytoplasmic helix. The KCNE1 intracellular segment interacts with HelixC's dimer-of-dimers, and the HelixD tetramer binds with Yotiao (protein not shown) to facilitate IKs phosphorylation. In addition, HelixC and HelixD are suggested to play a role in subunit dimerization and tetramerization, respectively (26). The inset (bottom left) shows the coordinate system of IKs (gray; side and bottom views) in the membrane (yellow). (B) An expanded view of the TM S1–S6 arrangement is shown. (C) A top view (without CaM and KCNQ1 C-terminus) and (D) bottom view of IKs are shown. The structural components and identifying symbols are color coded. S4S5L, S4-S5 linker; CaM, Apo-Calmodulin.