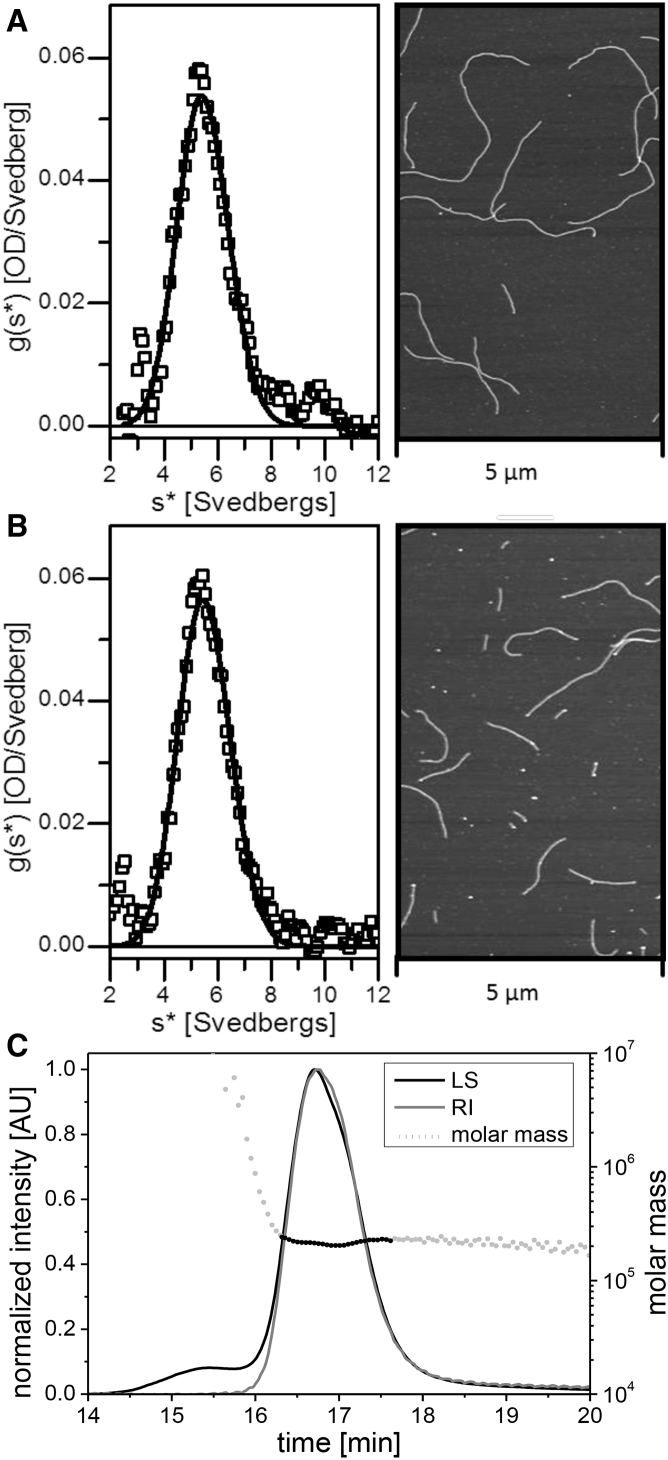
Figure 3.
Characterization of soluble vimentin complexes in tetramer buffer. (A) Sedimentation velocity ultracentrifugation shows vimentin renatured in tetramer buffer (left panel). After initiation of assembly, filaments were visualized by atomic force microscopy (right panel). (B) Sedimentation velocity ultracentrifugation shows the products obtained after dialysis of the filaments shown in (A) back into tetramer buffer (left panel). These complexes were subjected to another round of assembly, and the resulting filaments were again visualized by atomic force microscopy (right panel). (C) Vimentin renatured into tetramer buffer was subjected to size-exclusion chromatography, and the eluted protein was analyzed by multiangle light scattering (SEC-MALS). Recorded were the light-scattering signal (LS) and the protein-absorption signal (RI), with the left axis in arbitrary units (AU). Dotted line: molar mass. The prepeak between 15 and 16 min is caused by nonspecific particles.