FIGURE 5.
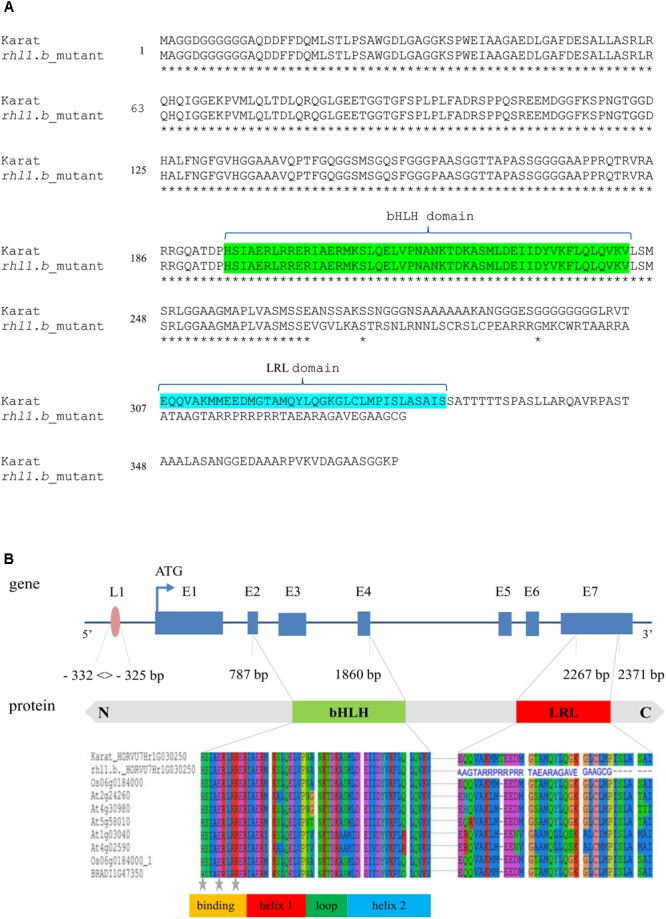
(A) The alignments of a putative protein sequences encoded by HORVU7Hr1G030250 (HvRhl1) gene for rhl1.b mutant and its parent variety ‘Karat’. Identical amino acids are marked by asterisks. bHLH and LRL domains are marked in green and blue, respectively. (B) The structure of HORVU7Hr1G030250 gene and the scheme of HORVU7Hr1G030250 protein domains. Dashed line represents the spliced intron in the wild type ‘Karat’. Blue boxes and lines represent exons and introns, respectively. Parts of exons 2nd and 4th and the whole exon 3rd encode the bHLH domain. Part of exon 7th encodes the LRL domain. L1, motif of L1 box-like sequence 5′-TAAATGT-3′ in the promoter region of the gene. N, C, N and C protein terminus, respectively. Below the alignment of the bHLH and LRL protein domains of HORVU7Hr1G030250 sequence from ‘Karat’ and rhl1.b mutant together with several A. thaliana, O. sativa, and B. distachyon homologous proteins are provided. The predicted protein sequence of rhl1.b mutant has an incorrect amino acid sequence (blue letters) in the region which corresponds to LRL domain in the wild type protein. Gray stars – conserved amino acid residues which are important for the contact with a nucleotides in DNA.
