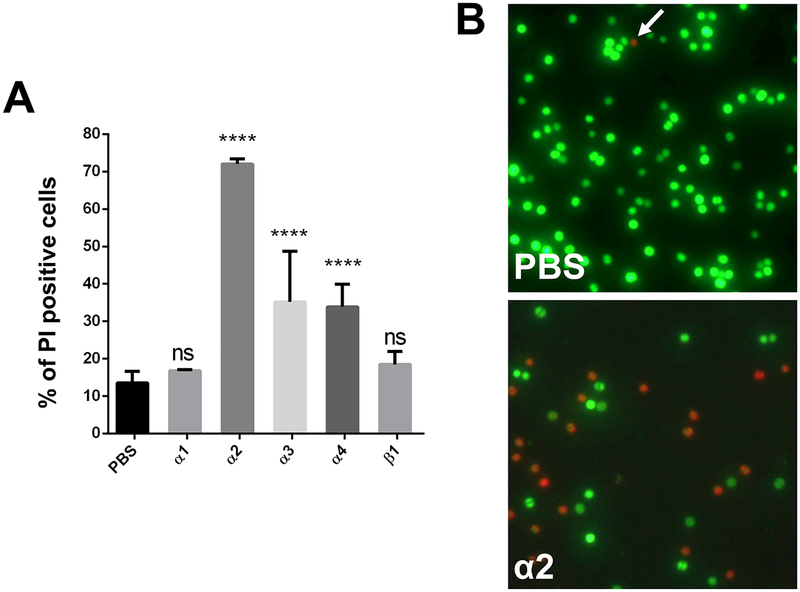
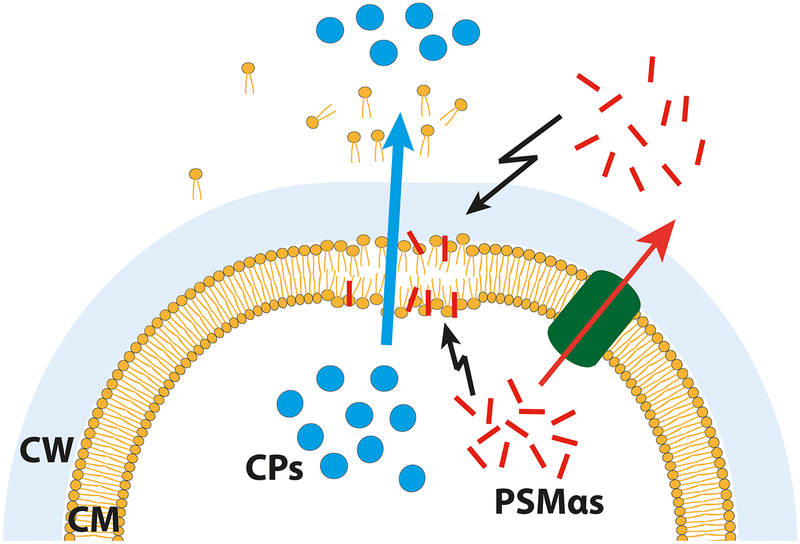
Figure 5: Monitoring of cytolytic effect of PSMs on S. aureus USA300 cells.
(A) Percentage of dead cells after treatment with PSM peptides. (B) Fluorescence microscopy of propidium iodide (red) and SYTO 9 (green) stained cells, either untreated or treated with PSMα2. Note: Propidium iodide positive cells (red) have damaged/leaky cell membranes. Scale bar represents 10 μm. (C) Proposed model for PSMα mediated excretion of cytoplasmic proteins. Either intracellular, as well as extracellular, PSMα peptides cause membrane perturbations and weaken the membrane integrity of S. aureus cells. This weakening causes cell leakage and therewith excretion of cytoplasmic proteins and other cytoplasmic compounds. Explanation: Cytoplasmic proteins, blue circles; PSMs, red rods; Pmt transporter, green tunnel; CM, cytoplasmic membrane; CW, cell wall. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. For all graphs, each data point is the mean value ± SD (n = 3) *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; and ****p < 0.0001, by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest.