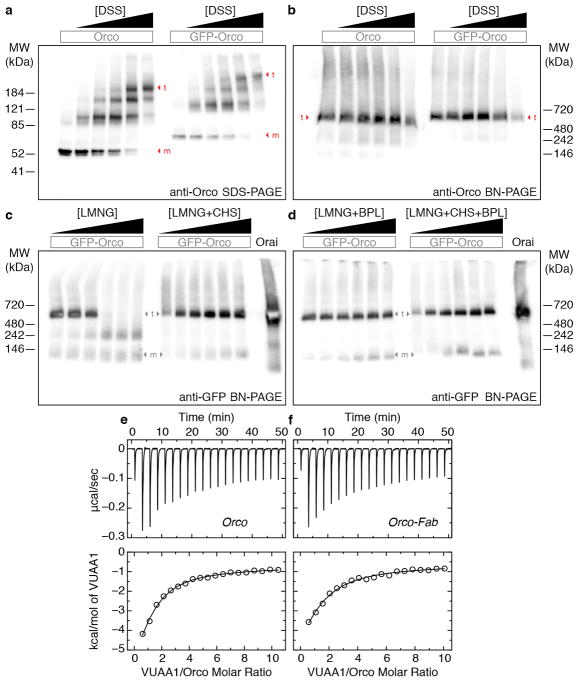
Extended Data Fig. 3. Stoichiometry and ligand binding of the Orco homotetramer.
a, Western blot of cross-linked Orco in transfected HEK293 cells. SDS-PAGE showing a ladder of four bands that appears with both GFP-tagged and untagged Orco after treatment with increasing concentration of the amine cross-linker disuccinimidyl suberate (DSS). Monomer (m) and tetramer (t) bands are indicated. DSS concentrations were (μM): 0, 25, 75, 125, 250, 2500. b, Western blot of a Blue Native (BN)-PAGE63 gel of the same samples as in a showing that tetrameric Orco is present in all samples and higher-order aggregates are not induced by cross-linking. c,d Western blot of Orco extracted with increasing concentrations of detergent (LMNG) showed gradual loss of the tetrameric species. Addition of (c) CHS, (d) porcine brain polar lipid extract (BPL; Anatrace) or the combination of the two stabilized the Orco tetramer. LMNG concentrations were (% w/v): 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1. Concentration of CHS, BPL and the sum of CHS + BPL were added at 1/5 that of LMNG. GFP-labeled Orai (55 kDa)64 was used as a molecular weight marker as it is a hexamer with a similar total size as the Orco-GFP tetramer (340 kDa). The larger apparent molecular weights observed in BN-PAGE gels (b–d) reflect the additional mass of the micelle. Primary antibodies used were: anti-Orco clone 20F7 and anti-GFP (Life Technologies). Each experiment in this figure was repeated three times with similar results. The molecular weight markers on the native gels are approximate: they are from a separate gel run under the same conditions (see Supplementary Data). e,f, Representative baseline-corrected isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) data for (e) Orco (11 μM) and (f) Orco-Fab complex (10 μM) titrated with VUAA1. Integrated heats and fitted single-site binding isotherms are shown at the bottom. The number of binding sites per monomer was fixed at 1 and the dissociation constant (Kd), enthalpy of binding (ΔH), and heat associated with sample dilution (ΔQdil) were fit. The experiments were repeated three times each using Orco samples obtained from independent purifications. The average fitted thermodynamic parameters are as follows (mean ± s.d.). Orco: Kd = 13 ± 1 μM, ΔH = −8.3 ± 0.6 kcal/mol, ΔQdil = −1.0 ± 0.1 kcal/mol. Orco-Fab: Kd = 18 ± 2 μM, ΔH = −9.7 ± 0.4 kcal/mol, ΔQdil = −1.0 ± 0.2 kcal/mol.