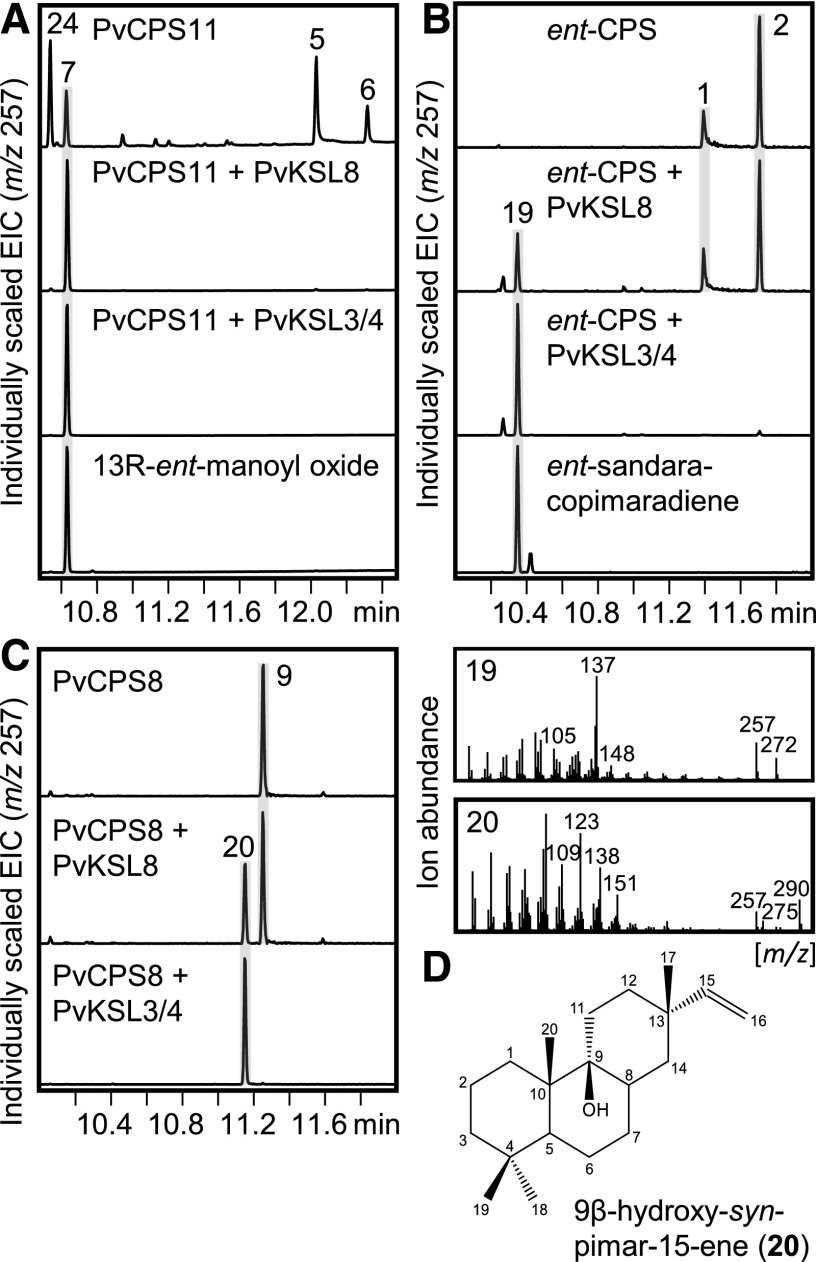
Figure 5.
Functional characterization of the promiscuous class I diTPSs PvKSL3/4 and PvKSL8. A to C, GC-MS traces of products resulting from E. coli coexpression assays of the class I diTPSs PvKSL3/4 and PvKSL8 with the ent-LPS PvCPS11 (A), the ent-CPS ZmAn2 (Harris et al., 2005; B), and the syn-CPS PvCPS8 (C). Individually scaled extracted ion chromatograms (EIC; m/z 257) are shown with the corresponding mass spectra of select diterpenoids. D, Structure of 9β-hydroxy-syn-pimar-15-ene as verified by NMR analysis. Numbered peaks are as follows: 1, ent-copalol (i.e. dephosphorylated ent-CPP); 2, unidentified diterpene; 5, ent-8β-labda-13E-en-8,15-diol (i.e. dephosphorylated ent-LPP); 6, ent-8α-labda-13E-en-8,15-diol; 7, 13R-ent-manoyl oxide; 9, syn-copalol; 19, ent-sandaracopimaradiene; 20, 9β-hydroxy-syn-pimar-15-ene; 24, 13S-ent-manoyl oxide.