Figure 1.
Genomic Position Analysis of pA+ and pA− RNA 3′ Ends
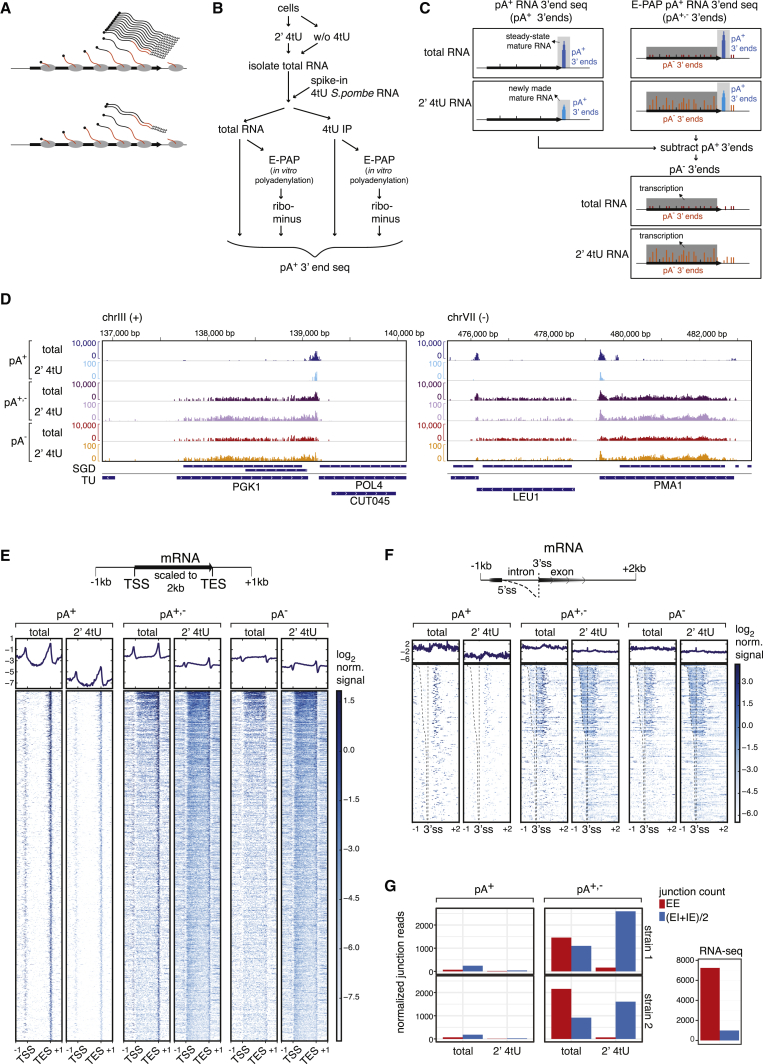
(A) Schematic representation of non-labeled (black) and metabolically labeled (red) fractions of total (top) or purified labeled (bottom) RNA.
(B) Experimental strategy as outlined in the main text.
(C) Workflow to derive pA− 3′ ends. Theoretical distribution of RNA 3′ ends in the 2′ 4tU and total samples are depicted as explained in the main text.
(D) Genome browser views of RNA 3′ ends around the PGK1 (left) and LEU1-PMA1 (right) loci. pA+ (top), pA+,− (middle), and pA− (bottom) log-scaled signals are shown from total and 2′ 4tU samples as indicated. Chromosomal coordinates and the strand for which data are shown are indicated on top. Annotations below each view region are from the Saccharomyces Genome Database (SGD; top), marking coding regions or mature isoforms of ncRNAs and transcribed regions according to Xu et al. (2009) (TU; bottom).
(E) RNA 3′ ends as in (D) but shown as metagene profiles (top panels) and heatmaps (bottom panels). Log2 values are shown between all mRNA (n = 5,170) TSSs and TESs rescaled to 2 kb with 1 kb of non-scaled upstream and downstream regions as schematized on top. Metagene profiles display the mean of log2 values at each position. Rows of the heatmap are sorted by descending signal of the 2′ 4tU pA− sample.
(F) Metagene profiles (top) and heatmaps (bottom) as in (E) but around introns of protein-coding genes (n = 282). Data were aligned to intron 3′ splice sites (3′ss), including regions of 1 kb and 2 kb up- and downstream, respectively (as schematized on top), without scaling to length. Regions were ordered by descending intron sizes and dashed lines indicating 5′ss and 3′ss.
(G) Quantification of exon-exon (EE), splice junction (exon-intron [EI] + intron-exon [IE]/2) read counts from pA+ and pA+,− samples as well as total and 2′ 4tU libraries as indicated for the two yeast strains (left panels). A similar quantification of regular RNA-seq data from a control S. cerevisiae strain is shown on the bottom right.