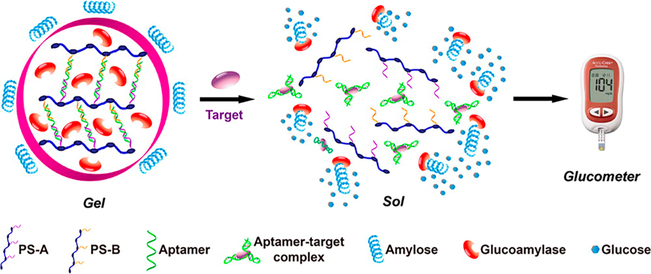
Figure 3.
An aptamer-cross-linked hydrogel with trapped glucoamylase is formed by hybridization of the aptamer and its partially complementary DNA polymer strands (PS-A and PS-B). When target molecules are introduced, the aptamers specifically identify the targets to form target−aptamer complexes, causing breakdown of the hydrogel and release of glucoamylase, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of amylose to produce a large amount of glucose for quantitative readout by the glucometer. Reprinted from ref 12. Copyright 2013 American Chemical Society.