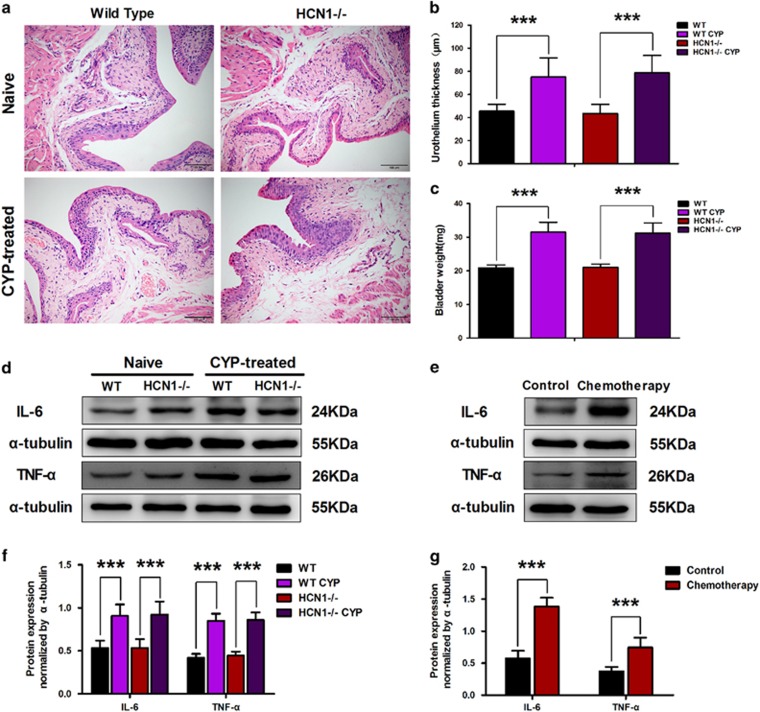
Figure 1.
Cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced cystitis in WT and HCN1−/− mice. (a) Characteristic inflammation was detected in histological bladder sections of CYP-treated WT and HCN1−/− mice. Urothelial thickness (b) and bladder weight (c) were significantly increased in both CYP-treated WT and HCN1−/− mice (data represent the mean±s.d., N=10, ***P<0.001, versus naive mice). (d, f) IL-6 and TNF-α protein expression levels in the bladders of both WT and HCN1−/− mice were significantly elevated when these mice were treated with CYP (data represent the mean±s.d., N=6, ***P<0.001, versus naive mice). (e, g) IL-6 and TNF-α protein expression levels were significantly enhanced in the bladder samples of patients undergoing chemotherapy (data represent the mean±s.d., N=5, ***P<0.001, versus control sample).