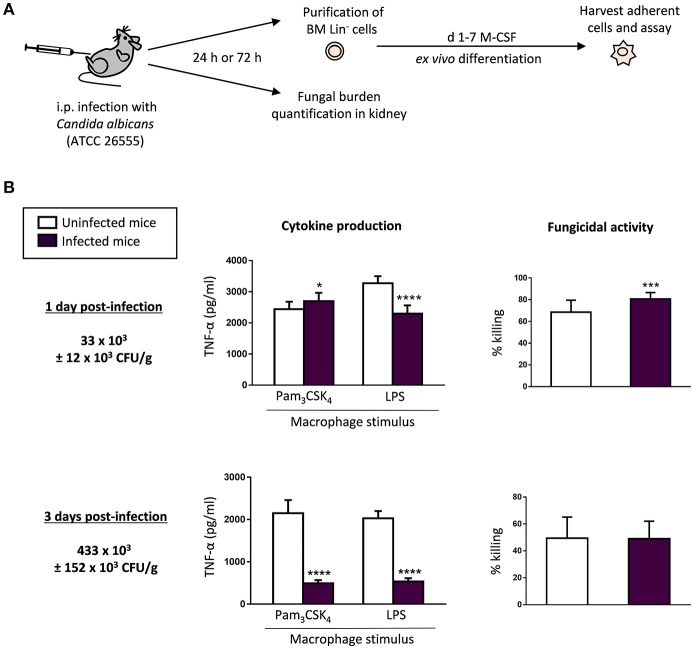
Figure 1.
C. albicans infection impacts the cytokine production and the fungicidal activity of the ex vivo produced macrophages. (A) Schematic protocol (as described in section Materials and Methods). WT mice were injected intraperitoneally with 45 × 106 yeasts of C. albicans ATCC 26555. 1 or 3 days post-infection mice were sacrificed to assess the outgrowth of the yeasts in the kidney, and to isolate the bone marrow. Lin− HSPCs were purified from bone marrow, plated at a density of 200,000 cells in 4 ml of culture medium containing SCF, M-CSF and amphotericin B, and incubated for 7 days to induce macrophage differentiation. (B) The fungal burden in the kidneys is expressed as CFUs per gram of tissue. For cytokine assays, macrophages were plated at a density of 50,000 cells in 200 μl of complete cell culture medium and challenged with Pam3CSK4 (100 ng/ml) or LPS (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. TNF-α levels in cell-free culture supernatants were measured by ELISA. For fungicidal activity determination, macrophages were plated at a density of 200,000 cells in 200 μl of complete cell culture medium and challenged with viable PCA2 yeasts at a 1:3 ratio (murine cell:yeast) for 1 h. C. albicans cells were also inoculated in culture medium without murine cells (control). After incubation, samples were diluted, plated on Sabouraud dextrose agar and incubated overnight at 37°C; CFUs were counted and killing percentages were determined as follows: % killing = [1 – (CFUs sample at t = 1 h)/(CFUs control at t = 1 h)] × 100. Triplicate samples were analyzed in each assay. Results are expressed as means ± SD of pooled data from two experiments. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 with respect to macrophages derived from control uninfected mice.