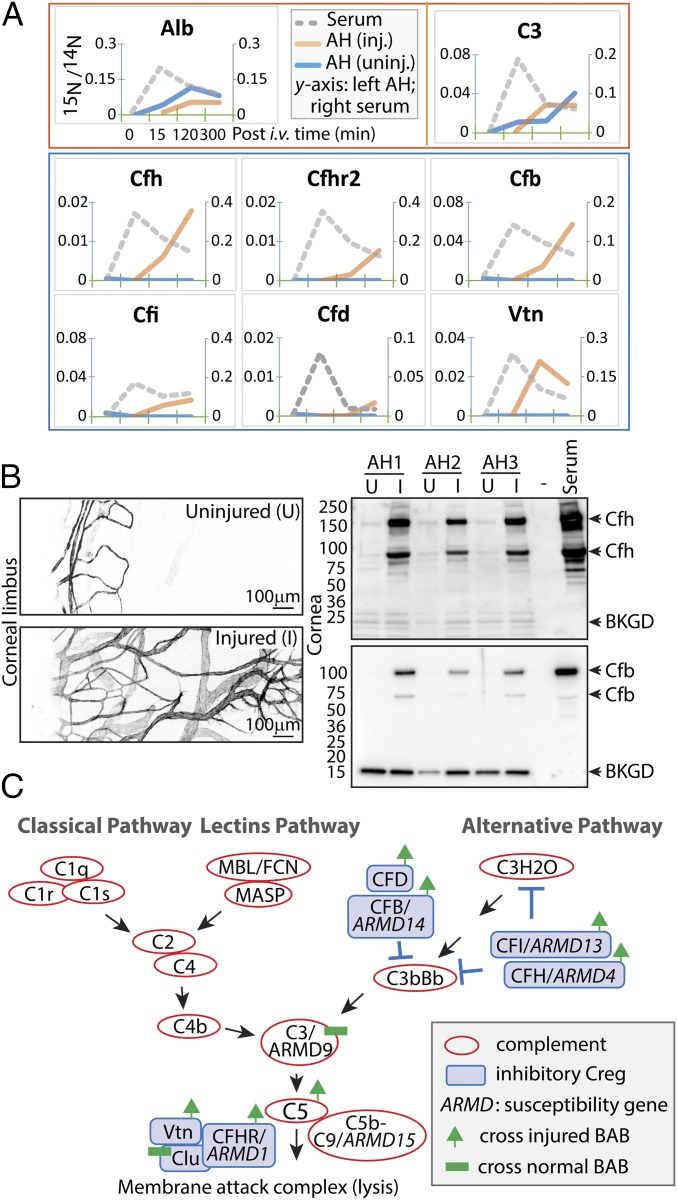
Fig. 4.
Complement regulatory proteins enter aqueous in wound healing. (A) From the top, the red box shows representative proteins of albumin and C3 that entered the aqueous of both injured and uninjured eyes (legends shown for albumin; 15N/14N ratios: left scale for aqueous and right scale for serum), and the blue box contains proteins that entered the injured eyes but not the uninjured eyes. (B) Unilateral corneal treatment with alkali was applied to mice, and corneal neovascularization was evident 2 wk later (compare the anti-CD31 images of uninjured and injured eyes). Aqueous proteins were extracted from individual eyes in three mice (AH1–3). Immunoblotting shows levels of Cfh and Cfb proteins. (C) The complement pathways in association with AMD. Red circles represent complement-activating proteins; blue boxes, complement regulatory proteins. Proteins associated with genetic susceptibility to AMD are annotated (ARMD1–15), and proteins with increased permeability in wound healing and proteins with constant barrier-crossing kinetics are indicated.