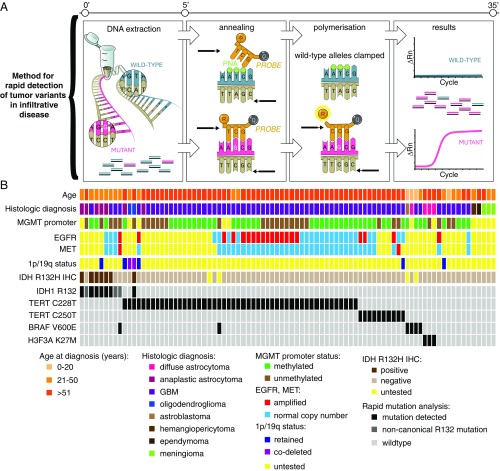
Fig. 4.
Method for detection of recurrent mutations noted in glioma allows for rapid molecular genotyping to guide intraoperative decision for use of targeted local therapy. (A) The rapid genotyping assay utilizes Taqman-based probes for fluorescence-based detection of mutant alleles with clamping of the wild-type allele amplicon via peptide nucleic acid oligonucleotides, allowing for detection of tumor variants to an allelic fraction of 1% within 30 min. (B) Validation of genotyping assay correlates mutation call for IDH1 R132, TERT promoter variants, H3F3A K27M, and BRAF V600E in 87 brain tumor specimens from a clinically annotated database. EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; GBM, glioblastoma; IHC, immunohistochemistry; MET, tyrosine-protein kinase Met; MGMT, O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase; PNA, peptide nucleic acid; Rn, normalized reporter value.