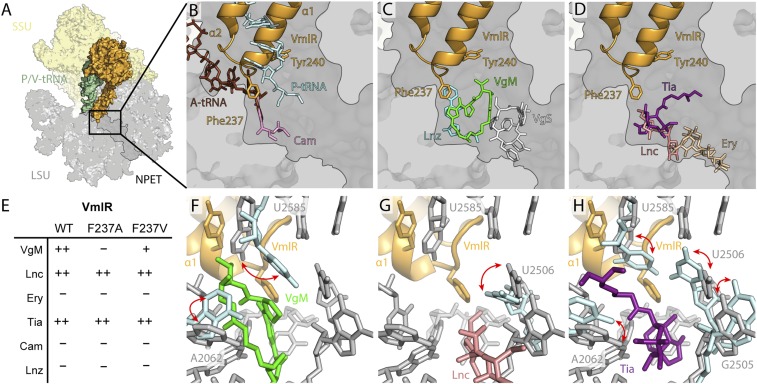
Fig. 4.
Interaction of VmlR at the peptidyltransferase center. Overview of VmlR (orange) and P/V-tRNA (green) on the ribosome (SSU, yellow; LSU, gray) (A) with transverse section of the LSU to reveal the nascent polypeptide exit tunnel (NPET) with VmlR (orange) superimposed (B–D) against A-site tRNA (brown) and P-site tRNA (cyan) from a pretranslocation state (39) and chloramphenicol (Cam, pink, PDB ID code 4V7U) (41) (B); virginiamycin M (VgM, green) and S (VgS, white) (PDB ID code 1YIT) (24) and linezolid (Lnz, cyan, PDB ID code 3DLL) (42) (C); lincomycin (Lnc, salmon, PDB ID code 5HKV) (25), tiamulin (Tia, purple, PDB ID code 1XBP) (26), and erythromycin (Ery, tan, PDB ID code 4V7U) (41) (D). (E) Summary of antibiotic resistance conferred by WT VmlR as well as VmlR variants F237A and F237V complementing a ΔvmlR strain of B. subtilis (see also SI Appendix, Fig. S6 A–F). (F–H) The conformation of selected 23S rRNA nucleotides (gray sticks) at the PTC in the presence of VmlR (orange) superimposed with with different nucleotide (cyan) conformations (indicated by red arrows) when virginiamycin M (VgM, green, PDB ID code 1YIT) (24) (F), lincomycin (Lnc, pink, PDB ID code 5HKV) (25) (G), and tiamulin (Tia, purple, PDB ID code 1XBP) (26) (H) are bound to the ribosome.