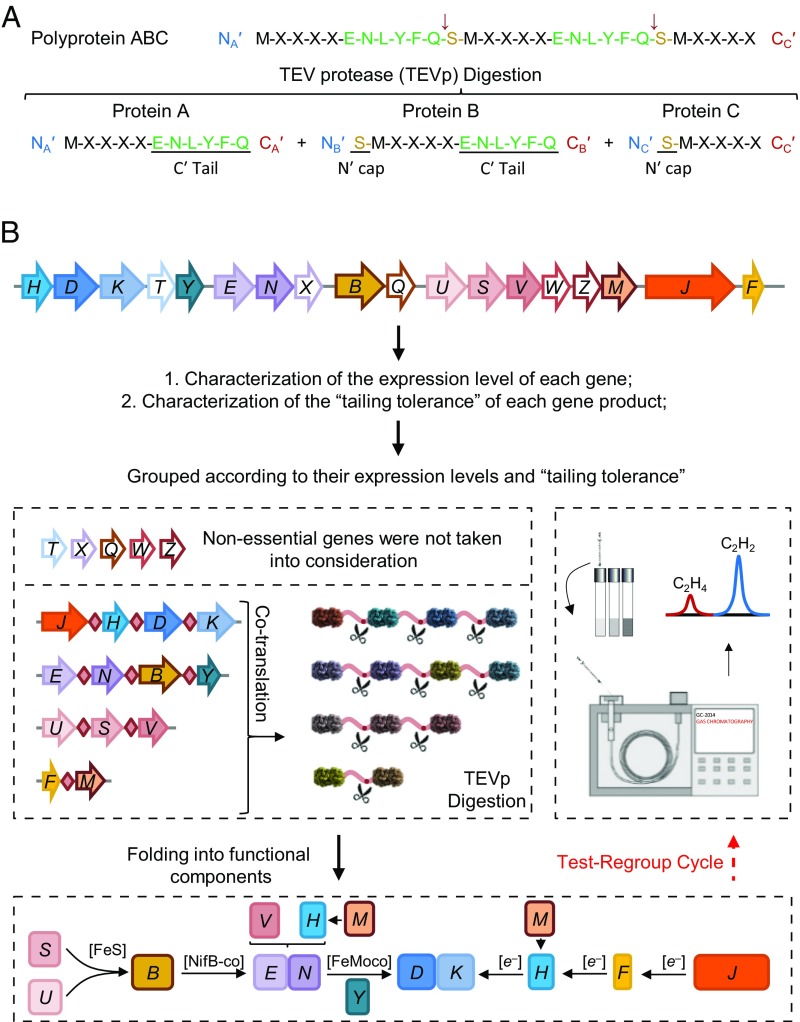
Fig. 1.
Process for reconstructing biological nitrogen fixation using the posttranslational protein splicing strategy. (A) Digestion of polyproteins by TEVp leads to a C-terminal ENLYFQ-tail for the lead protein A, an N-terminal S-cap for the last protein C, and both an N-terminal S-cap and a C-terminal ENLYFQ-tail for the sandwiched protein B. (B) Arrangement of structural and accessory nif genes in the reconstituted operon-based system (pKU7017) from K. oxytoca (5). The regulatory nifLA operon, which controls transcription from σ54-dependent nif promoters, is not included in this diagram (a detailed description of pKU7017 is provided in Materials and Methods). Essential nif genes were regrouped and assembled into giant genes based on their relative expression levels and tailing tolerance. Test-regroup cycles were carried out to select for optimal combinations of the polyprotein-based system that yielded nitrogenase activity as measured by the acetylene reduction assay.