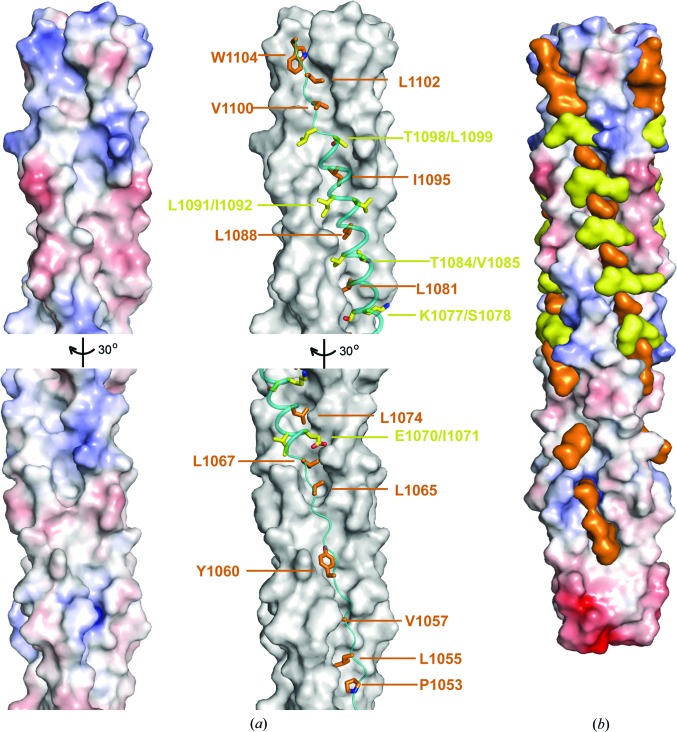
Figure 3.
Two types of hydrophobic interactions are observed between the HR1 and HR2 helices. (a) Left panel: electrostatic surface illustrating the hydrophobic cavities on the surface of the HCoV-229E 3HR1 core. The lower half of the 3HR1 core is rotated for better display of the hydrophobic cavities in this region. Right panel: HR2 helices are shown as teal ribbons on the dark grey surface of the HCoV-229E 3HR1 core. HR2 residues that bury their side chains completely into the cavities on HR1 are shown as orange stick models and HR2 residues that pack around 50% of the solvent-accessible surface of their side chains on ridges of HR1 are depicted as yellow stick models. (b) Surface representation of HR1 and HR2 helices illustrating that HR2 residues fit snugly onto the surface of the 3HR1 core, thereby filling hydrophobic cavities in HR1 and masking its hydrophobic surface. The 3HR1 core is shown as an electrostatic surface, and HR2 residues involved in hydrophobic interactions are depicted as orange (completely buried) and yellow (packing, ∼50% buried) surfaces, respectively.