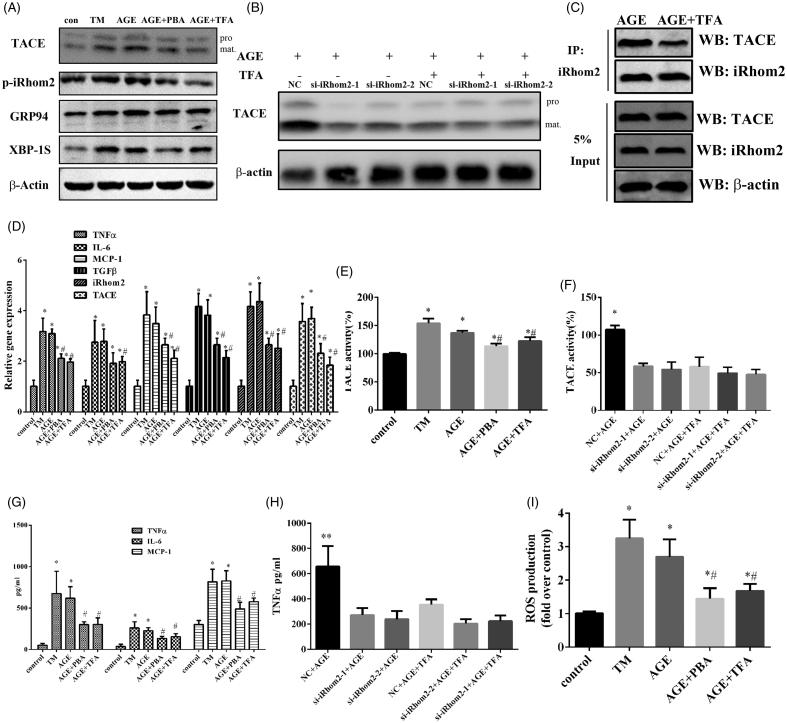
Figure 2.
TFA attenuates ER-stress and inhibits activation of iRhom2/TACE signalling induced by AGEs in HK-2 tubule epithelial cell. (A) Western blot analysis of the activation of iRhom2/TACE signalling and the ER stress markers XBP1S and GPR94 are shown, pro: pro-TACE, mat: mature TACE; (B) western blotting analysis protein level of TACE in HK-2 cells induced by AGEs when iRhom2 was knockdown treated with TFA or not, pro: pro-TACE, mat: mature TACE; (C) immunoprecipitation analysis of iRhom2 binds to TACE when treated with TFA; (D) real time PCR showed that TFA decreased expression of iRhom2, TACE and inflammatory cytokine genes in HK-2 induced by AGEs.*p < 0.05 vs. control, #p < 0.05 vs. AGE, n = 3; (E) TFA inhibited the activity of TACE in HK-2 induced by AGEs, *p < 0.05 vs. control, #p < 0.05 vs. AGE, n = 3; (F) both iRhom2 knockdown and TFA inhibited the activity of TACE in HK-2 induced by AGEs, *p < 0.05 vs. control, #p < 0.05 vs. AGE, n = 3; (G) measurement of the secretion of inflammatory cytokines in HK-2 by ELISA, *p < 0.05 vs. control, #p < 0.05 vs. AGE, n = 3; (H) measurement of the secretion of TNF-α in HK-2 by ELISA when iRhom2 was knockdown treated with TFA or not, **p < 0.01 vs. the other groups, n = 3; (I) TFA decreased ROS production in HK-2 induced by AGEs, *p < 0.05 vs. control, #p < 0.05 vs. AGE, n = 3.