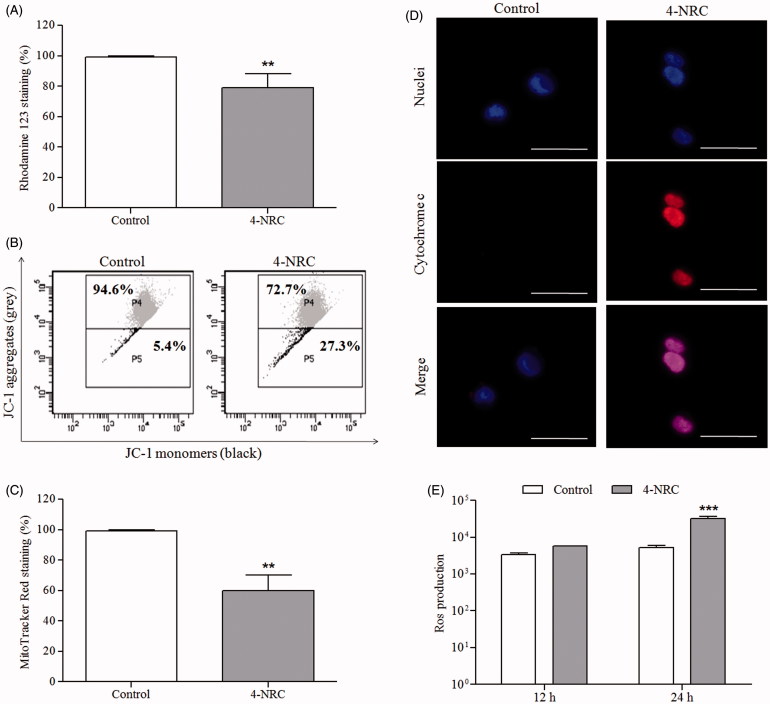
Figure 5.
Effects of 4-NRC on mitochondrial function and ROS production in K562 cells. Cells (1 × 106 cells/mL) were treated with 4-NRC (27 μM) for 24 h and mitochondrial function was analyzed by different assays as follows: (A) 4-NRC-induced Δψm changes were previously evaluated by rhodamine 123 staining; (B) mitochondrial depolarizing ability of 4-NRC was confirmed by JC-1 staining: representative histogram shows viable cells with mitochondria-aggregated JC-1 (normal Δψm) and apoptotic cells with monomeric and cytosolic JC-1 of control and 4-NRC groups; (C) reduction of mitochondrial mass promoted by 4-NRC was evaluated by Mitotracker Red staining; and (D) cytochrome c release by mitochondria of untreated cells and cells treated with 4-NRC was determined by microscopy: the nuclei were visualized by Hoechst staining and merging the cytochrome c and nuclei representative images were carried out (630 × magnification). Dotted circle represents cytochrome c not detectable in control cells. Scale bars =25 μm. (E) Intracellular ROS generation analysis in K562 cells treated with 4-NRC using a fluorimetric probe, 2,7-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA). Results represent the mean ± SD. Data are representative of three independent experiments (**p < 0.001 and ***p < 0.0001 vs. control).