Fig. 3. ALRN-6924 blocks MDM2- and MDMX-p53 protein-protein interactions and activates the p53 pathway in AML.
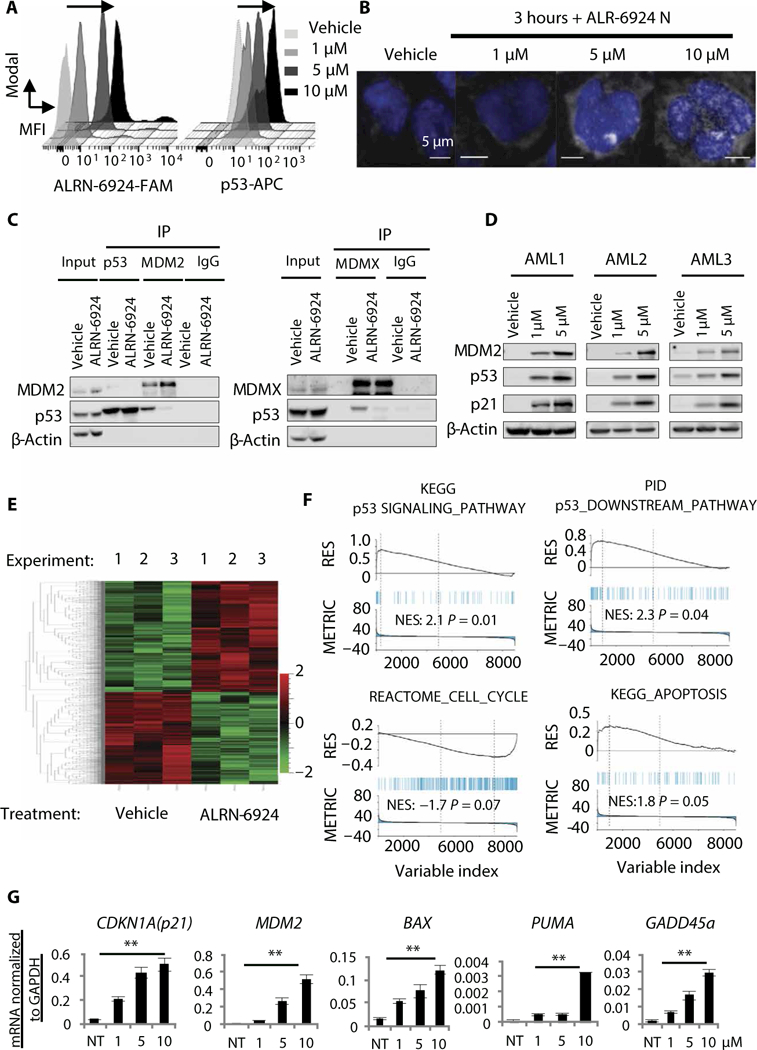
(A) Intracellular staining of FAM-labeled ALRN-6924 and p53-APC 3 hours after treatment with vehicle or ALRN- 6924 at the indicated doses [a representative histogram is shown, black arrow denotes rightward shift (increase) in mean fluorescence intensity (MFI)]. (B) High-resolution fluorescence microscopy of MOLM13 cells treated with FAM- labeled ALRN-6924 3 hours after treatment with the indicated doses (shown is a representative image). (C) Coimmuno- precipitation with anti-MDM2 (left), anti-p53 (left) and anti-MDMX (right) antibodies or immunoglobulin G (IgG) isotype control using MOLM13 cellular extracts followed by Western blot analysis with anti-p53, anti-actin, anti-MDM2, or anti- MDMX antibodies. IP, immunoprecipitation. (D) Western blot analysis showing expression of p53 and p53-target proteins (p21 and MDM2) in primary patient AML cells (representative blots are shown). (E) Hierarchical clustering of genes differentially expressed in MOLM13 cells after exposure to 1 μM ALRN-6924 for 6 hours compared to vehicle-treated cells (n = 3). (F) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) showing the top gene signatures differentially expressed in response to ALRN-6924. (G) Targeted gene expression analysis by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) of p53 target genes [CDKN1A (p21), MDM2, BAX, PUMA, and GADD45a] in response to increasing concentrations of ALRN-6924 in MOLM13 cells (n = 3, shown as the mean ± SD; **P < 0.01). KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; PID, Pathway Interaction Database; NES, normalized enrichement score; NT, no treatment.
