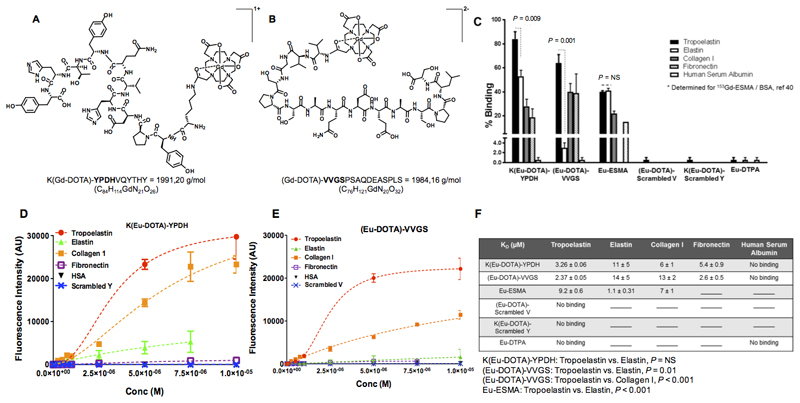
Figure 1. Chemical structures and in vitro binding experiments of the tropoelastin-binding probes.
A, B, Chemical structures of the probes. C, In vitro binding show superior discrimination between tropoelastin and mature elastin for the (Eu-DOTA)-VVGS compared with K(Eu-DOTA)-YPDH whereas Eu-ESMA binds equally to tropoelastin and mature elastin. The new probes show less binding towards other proteins compared with tropoelastin whereas the scrambled peptides do not bind to tropoelastin. Eu-DTPA shows little binding to tropoelastin, collagen I and human serum albumin. D-E, The saturation binding plots show that both probes bind to tropoelastin whereas no binding to HSA was observed. Finally, no binding of the scrambled probes to tropoelastin was observed. F, The KD values showed that the probes have high affinity for tropoelastin. Statistical differences between Kd values are shown.
No binding signifies that the data could not be fit, and lines indicate that the assay was not performed (n=2 for elastin, n=3 for all other proteins). Eu: europium(III), ESMA: elastin-specific MR contrast agent.