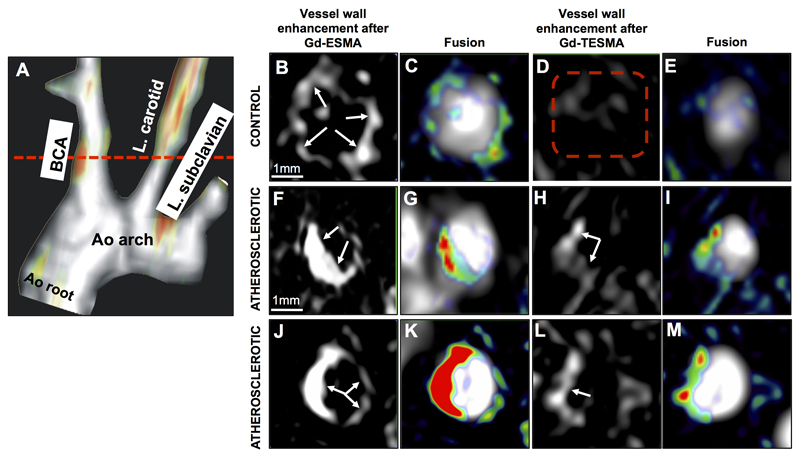
Figure 3. In vivo MRI comparison of vessel wall enhancement using the elastin (ESMA) and tropoelastin (TESMA) binding contrast agents in mice.
A, Fused MIP reconstructed MRA and DE-MRI images after administration of Gd-TESMA show focal uptake of Gd-TESMA in the BCA of an atherosclerotic ApoE-/- mouse. B-E, MRI images of the BCA acquired from a control animal, scanned 24h apart, showed vessel wall uptake of Gd-ESMA (B, C) but no uptake of Gd-TESMA (D, E) due to the lack of tropoelastin in the absence of disease. F-M, MRI images of the BCA acquired from two different diseased animals showed enhancement of the vessel wall after administration of both agents due to the presence of both cross-linked elastin and tropoelastin in the atherosclerotic lesion. MIP: maximum intensity projection, BCA: brachiocephalic artery. L.: left, Ao: aortic, (n=5 per group).