Figure 7. Read-through transcription into B compartment chromatin results in enhanced transcription factor binding.
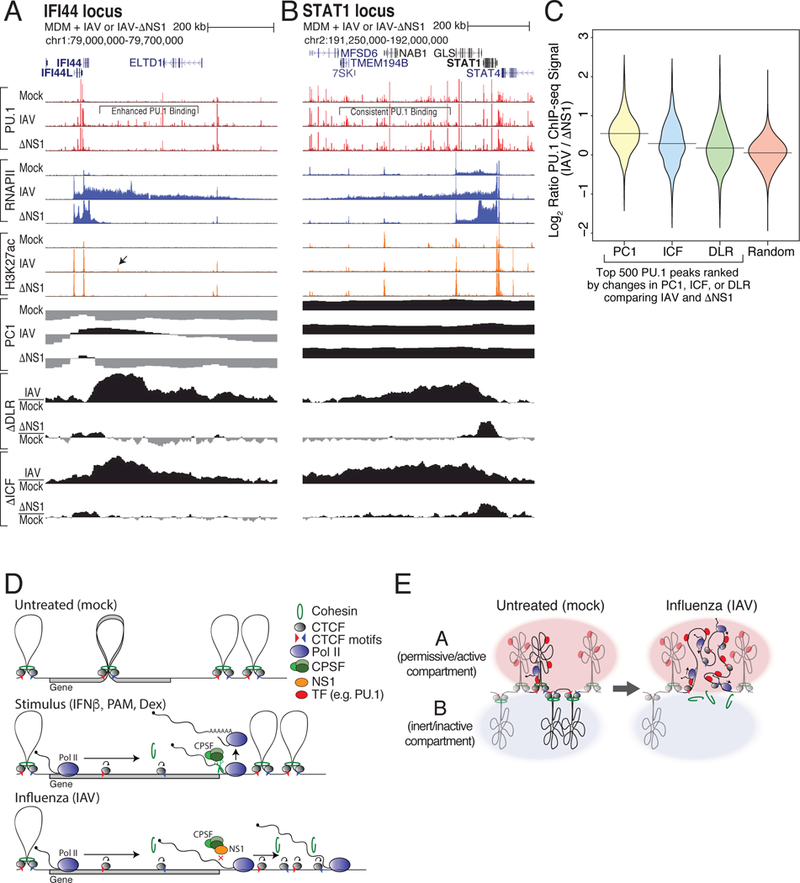
(A,B) Transcription factor binding is increased where B-to-A compartment changes occur. ChIP-seq tracks for PU.1, RNAPII, and H3K27ac at the IFI44 (A) and STAT1 (B) loci in macrophages infected with IAV, IAV lacking NS1 (ΔNS1), or mock. PC1 values and changes in ΔDLR and ΔICF are depicted for each locus. Black arrow highlights new H3K27ac-marked PU.1 site. (C) Distribution of log2 binding ratios between IAV and ΔNS1 conditions for the 500 PU.1 ChIP-seq peaks in regions exhibiting the largest changes in ΔPC1, ΔICF, ΔDLR, or random regions. (D) Model of RNAPII elongation-mediated dissolution of chromatin structure by removal of cohesin at CTCF sites. (E) Model of RNAPII elongation-mediated switching of regions from the B to the A compartment following IAV infection. See also Figure S7.
