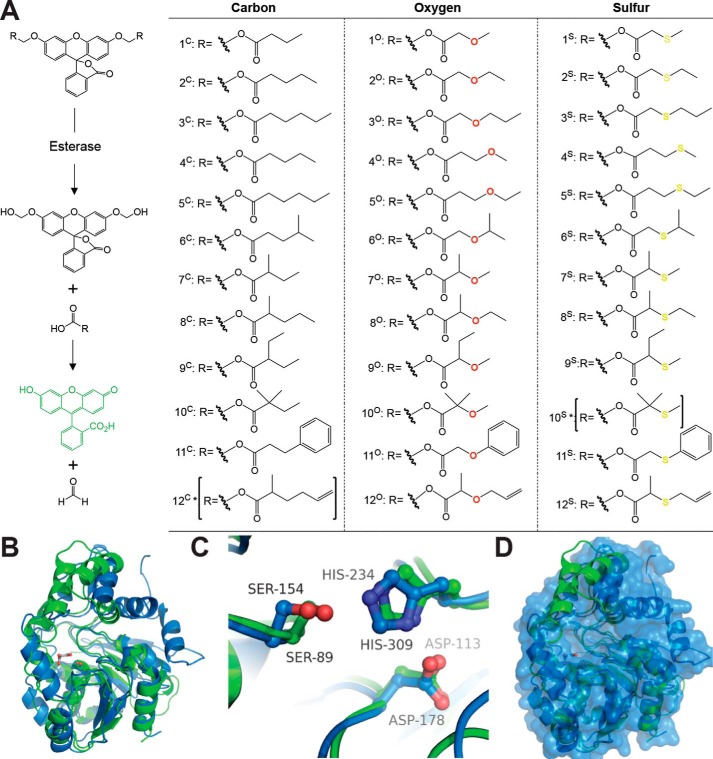
Figure 1.
Fluorogenic SAR library. A, fluorogenic library of acyloxymethyl ether fluorescein derivatives. Each derivative remains nonfluorescent until activated by an esterase exposing the highly fluorescent fluorescein scaffold (16, 35, 41, 42). Removal of the ester functionalities by an esterase leads to a hemiacetal intermediate, which spontaneously decomposes in water to free fluorescein and formaldehyde (16). Derivatives were designed in 12 series based on changes in chain length, branching, polarity, and sterics. Each series contains carbon, oxygen, and sulfur versions to investigate the importance of hydrogen bonding, polarity, and electron withdrawing character to enzyme activation. Sets of identical compounds 2C/4C and 3C/5C are given different identifiers only for the sake of clearly presenting the C versus O versus S series in this figure. All of the derivatives were synthesized using the recently published synthetic procedure, and full chemical characterization is given in the supporting Methods. Two derivatives (10S and 12C, indicated with asterisks) were not synthesized. B, overall structural alignment of ybfF (green; PDB code 3BF8) (56) and Rv0045c (blue; PDB code 3P2M with modeled dynamic loop) (42, 55). Esterases are shown in cartoon representations with the catalytic serine shown in sticks and colored by atom type. A malonate molecule (gray) from the ybfF structure is included to demarcate the binding pocket (56). Structures were aligned using PyMOL based on total global structural alignment of individual subunits. C, catalytic triad alignment of ybfF and Rv0045c. The catalytic triad is shown in sticks and colored identically to B. D, variation in cap domain of ybfF and Rv0045c. Shown is a surface representation of Rv0045c (blue) with a cartoon representation of ybfF (green). The divergence in cap domain structures is illustrated based on the green helices from ybfF that protrude from the Rv0045c surface.