Figure 6.
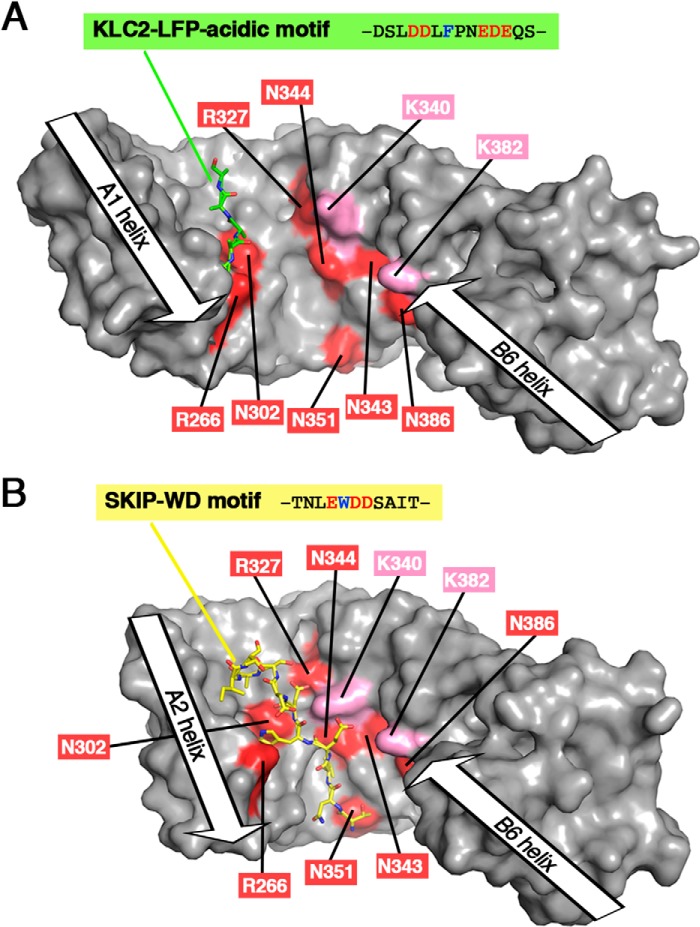
Comparison of the binding sites of the LFP-acidic motif and the SKIP-WD motif with the JIP1-binding site footprint. A, 3D structure of KLC2-TPR bound to its LFP-acidic motif (PDB code 5FJY (14)). B, 3D structure of KLC2-TPR bound to SKIP-WD motif (PDB code 3ZFW (16)). In the KLC2-TPR:SKIP-WD motif complex structure, the A1 helix is not present in the KLC2-TPR fragment crystallized, whereas the B1 helix is not modeled due to electron density absence; thus, the TPR1 motif is absent from the 3D structure. Both KLC2-TPR molecules are shown with a surface representation in gray. KLC1-TPR residues that are critical for JIP1 binding are highlighted in red (residues in proximity to JIP1 are indicated in pink) and labeled with KLC1 numbering. The LFP-acidic motif and the SKIP-WD motif are shown in sticks and colored in green and yellow, respectively. Orientation is conserved with that of Fig. 5D (superposition is done on the TPR2 motif), but because of differences in TPR domain closure, residue positions are slightly different with respect to each other.