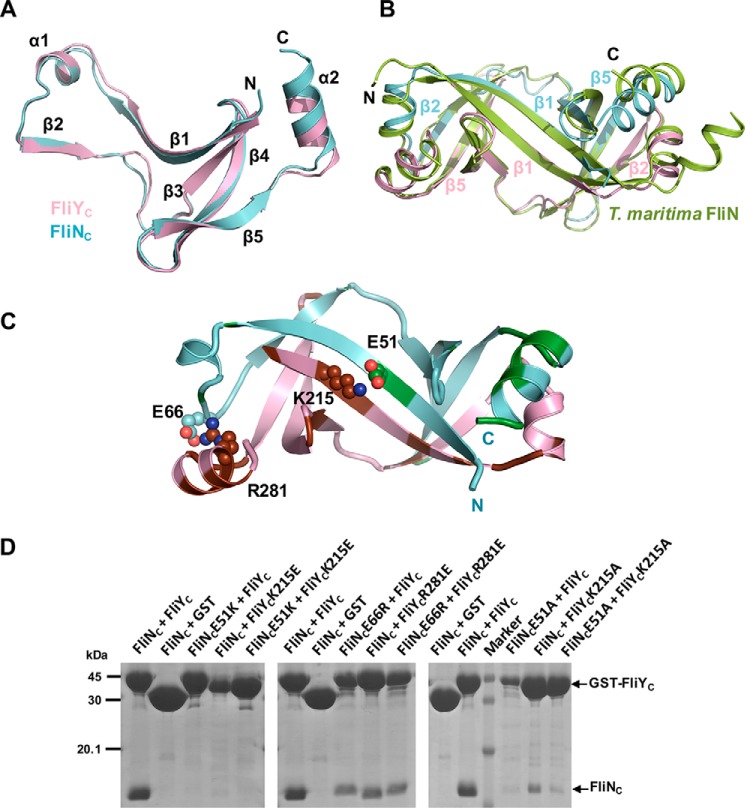
Figure 5.
Crystal structure of FliNC–FliYC. A, FliNC (pink) and FliYC (cyan) share high structural homology, comprising a platform of four antiparallel β-strands and a β1-α1-β2 protrusion. B, the superimposition of FliNC–FliYC to FliN homodimer of T. maritima (PDB code 1O6A). Heterodimer formation was mediated via the protrusion of FliYC or FliNC packed against the platform of FliNC or FliYC, especially via the β1–β1 and β2–β5 interactions. C, interaction of FliYC and FliNC. FliN- and FliY-specific residues are colored in green and brown, respectively. The residues that formed salt bridges are shown as spheres. D, effect of FliN or FliY mutations on complex formation. The GST-FliYC WT or mutants were coexpressed with His6-FliNC, and the FliY–FliN complexes were captured by GST resin.