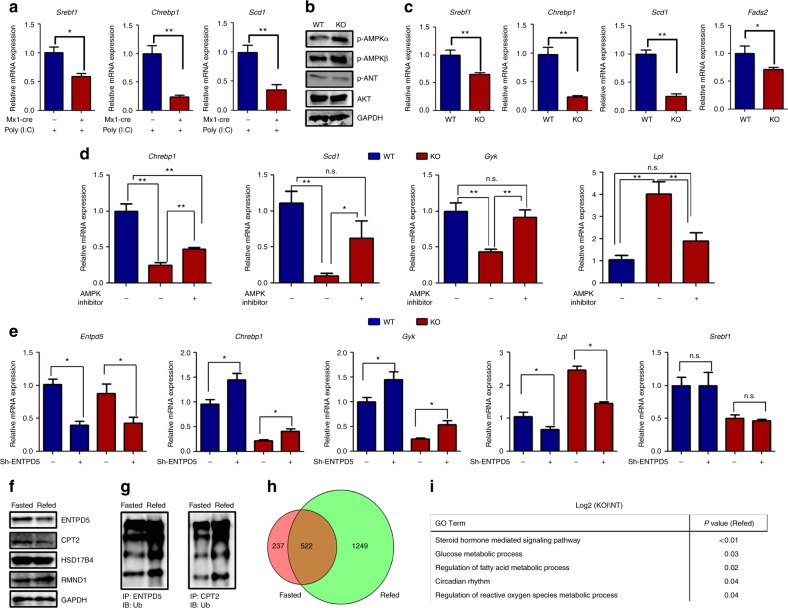
Fig. 6.
HRD1-mediated ubiquitination reprograms liver metabolic response partially through ENTPD5-AMPK pathway overactivation. a Relative mRNA of Srebf1, Chrebp1, and Scd1 of HRD1flox/flox (WT) and HRD1flox/flox Mx1-Cre+ mice 2 days after polyI:C injection (n = 5 for each group). b, c WT and HRD1Alb hepatocytes were isolated and cultured overnight. mRNA levels of Srebf1, Chrebp1, Scd1, and Fads2 (b) and AMPK and AKT activity were measured (c). d WT and HRD1Alb mice were fasted overnight and refed for 1 h and then administered with AMPK inhibitor for additional 3 h. Hepatic mRNA levels of Chrebp1, Scd1, Gyk, Srebf1, Lpl, and Acot9 were measured (n = 5 for each group). e WT and HRD1Alb hepatocytes were infected with lentivirus to specifically knockdown Entpd5. Two days after infection, hepatic mRNA levels of Entpd5, Hrd1, Chrebp1, Gyk, Lpl, and Srebf1 were measured (n = 5 for each group). f Hepatic ENTPD5, CPT2, RMND1, and HSD17B4 protein levels were measured in the fasted and refed conditions. g Ubiquitination levels of ENTPD5 and CPT2 were measured in the fasted and refed conditions. h Differential genes in the fasted and refed genes were overlapped. i Metabolic functions of the genes from h. Data are representative of three independent experiments (mean ± s.d.). *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01 by unpaired Student’s t test