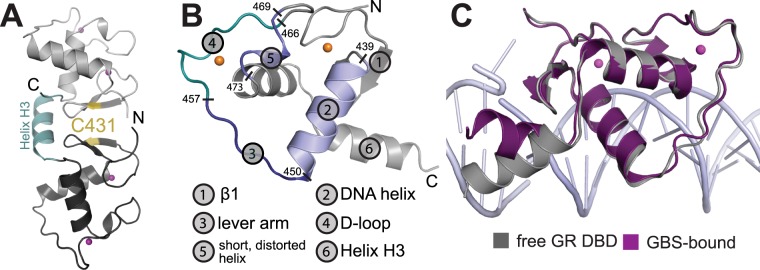
Figure 1.
Crystal structure of the DNA-free GR DBD. (A) Dimerization via formation of a disulfide between adjacent C431 residues. (B) Overall structure of the free GR-DBD with important structural elements highlighted. (C) The orientation of helix H3 differs between the free DBD and the DNA-bound state. In the DNA-bound state H3 lies across the major groove and makes interactions with the DNA phosphate backbone. The conformation of H3 found in the free state is rotated by ~60 degrees so that the helix lines up perpendicular to the major groove.