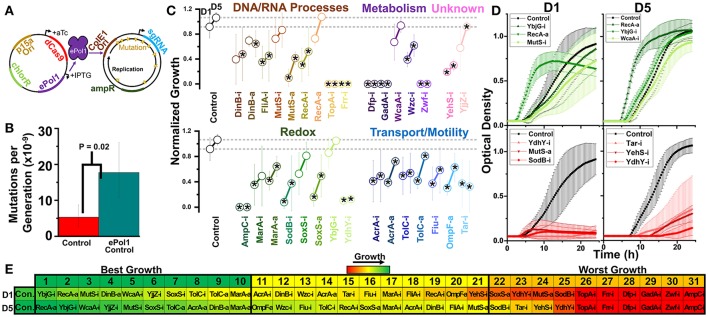
Figure 7.
Design of a hyper-mutator strain of E. coli for targeted error-prone replication of the sgRNA plasmid, and subsequent growth of these strains in 1.0% vol/vol n-butanol exposure. (A) We move dCas9 and dCas9-ω onto a plasmid expressing IPTG inducible error-prone Pol1 in a strain of E. coli expressing temperature-sensitive native Pol1. During growth at 37°C, error-prone Pol1 is expressed, causing low fidelity replication of plasmids with the ColE1 ori. This imparts significant mutations of the sgRNA plasmids with minimal impact on the dCas9/dCas9-ω plasmid or genome at large. (B) Whole-genome mutation rates of the control strain and the hyper-mutator control strain. Error bars represent the standard deviation of 32 technical replicates. A two-tailed type II t-test was used to calculate the statistical difference between the strains. (C) Normalized growth (maximum OD/starting OD) of hyper-mutator E. coli harboring CRISPR gene perturbations during 1.0% vol/vol n-butanol exposure. Change in the growth of each strain over 5days of exposure, with quantification on days one (D1) and five (D5). Strains are organized based on pathways affected by perturbation. Dashed lines extend from the control for each experimental day. A two-tailed type II t-test was used to calculate significance (as indicated by *P < 0.05) relative to the control on the same experimental day. Error bars represent the standard deviation of four biological replicates. (D) Growth curves of the three strains growing to the highest levels (green, top) and lowest levels (red, bottom) on D1 and D5. (E) Organized rankings of strains with the highest growth reached on each day, with the color scale to indicate relative growth. The top 10 and bottom 10 are indicated as “best growth” and “worst growth,” respectively.