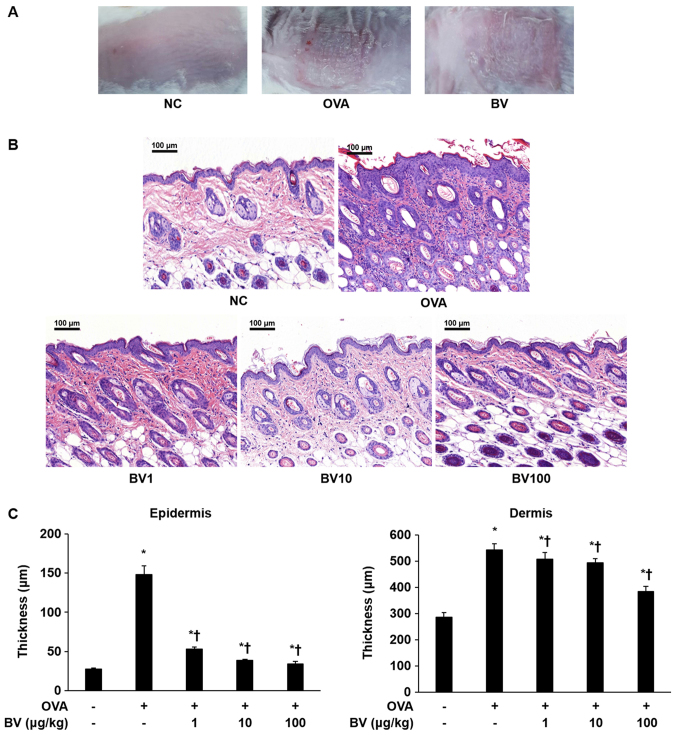
Figure 1.
BV inhibits inflammation in OVA-induced inflammatory skin disease. OVA was used to induce atopic dermatitis-like inflammatory skin disease through intraperitoneal inoculation and patch attachment. BV was intraperitoneally inoculated during OVA induction. (A) Skin lesions of each group. (B) Hematoxylin and eosin staining: Representative images of histological analysis, exhibiting increased epidermal and dermal thickness, and increased number of invasive inflammatory cells in the dorsal skin specimens; however, this increase was reduced in the BV administration group. Magnification, ×200; scale bars, 100 µm. (C) The thickness of the epidermis and dermis was measured. The results are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean of least 10 random fields per section. *P<0.05 vs. NC group; †P<0.05 vs. OVA group. BV, bee venom; OVA, ovalbumin; BV group, OVA with BV treatment (1, 10 and 100 µg/kg); NC, normal control; OVA, ovalbumin; BV, bee venom.