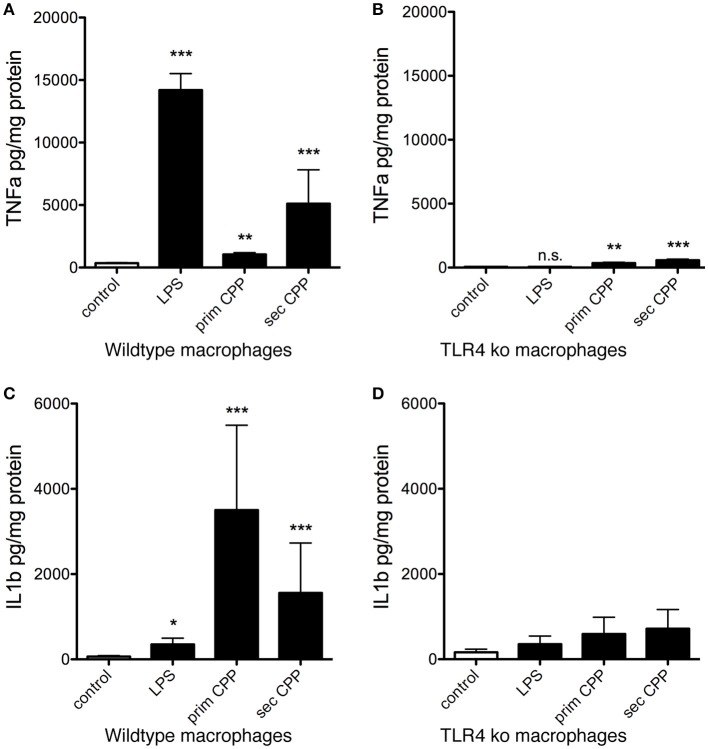
Figure 8.
CPP-induced inflammatory cytokine secretion by macrophages is TLR4 dependent. Serum-starved wildtype and TLR4-deficient macrophages (TLR ko) where treated with LPS, primary or secondary CPP. (A,B) After 6 h stimulation, inflammatory cytokine TNFα secretion was determined in culture supernatants by ELISA. Secondary CPP caused stronger TNFα secretion than primary CPP. TLR4 ko macrophages showed 10-fold reduced TNFα secretion compared to wildtype macrophages suggesting a major contribution of TLR4 signaling in CPP-triggered TNFα secretion. Nevertheless, CPP-stimulated TLR4 ko still secreted higher amounts of TNFα compared to untreated control (prim CPP p < 0.01, sec CPP p < 0.001) suggesting a minor contribution to overall TNFα secretion of a TLR4-independent pathway. (C,D) After 16 h stimulation, supernatant IL-1β secreted by LPS-primed wildtype macrophages treated with primary CPP was twice as high as treated with secondary CPP. Both values were significantly higher than in wildtype macrophages treated with buffer control or with LPS. TLR4-deficient macrophages show a slight increase in IL-1β processing after the treatment with both types of particles. Overall, inflammatory cytokine secretion was strongly reduced in TLR4 ko. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.