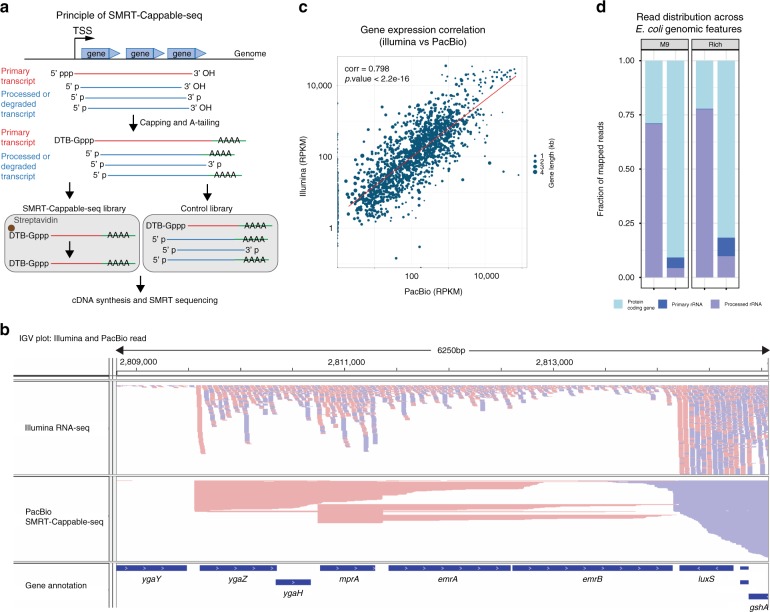
Fig. 1.
SMRT-Cappable-seq identifies full-length transcripts in bacteria. a Schema of the SMRT-Cappable-seq methodology. 5′ triphosphorylated transcripts are capped with a desthio-biotinylated (DTB) cap analog and bound to the streptavidin beads to specifically capture primary transcripts starting at TSS. The polyadenylation step (A-tailing) ensures the priming of the anchored poly dT primer for cDNA synthesis at the most 3′end of the transcript. b Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) representation of the mapping of SMRT-Cappable-seq reads (top) compared to Illumina RNA-seq reads (bottom) in the mprA locus. Forward oriented reads are labeled in pink, reverse oriented reads are labeled in blue. c Comparison between gene expression level in Read counts Per Kilobase of transcript, per Million mapped reads (RPKM) for Illumina RNA-seq and SMRT-Cappable-seq. The Spearman’s rank correlation is 0.798 (p value < 2.2e-16). Point size denotes the size of the gene (in kb). d Fraction of reads mapped to protein coding genes (light blue), primary rRNA (dark blue), and processed rRNA (purple) for both M9 and Rich growth conditions (left panel and right panel, respectively). Reads mapped to primary rRNA are defined as reads which start at a known TSS of a primary rRNA transcript2. Processed rRNAs correspond to reads mapped to the rRNA genes but do not start at these TSSs