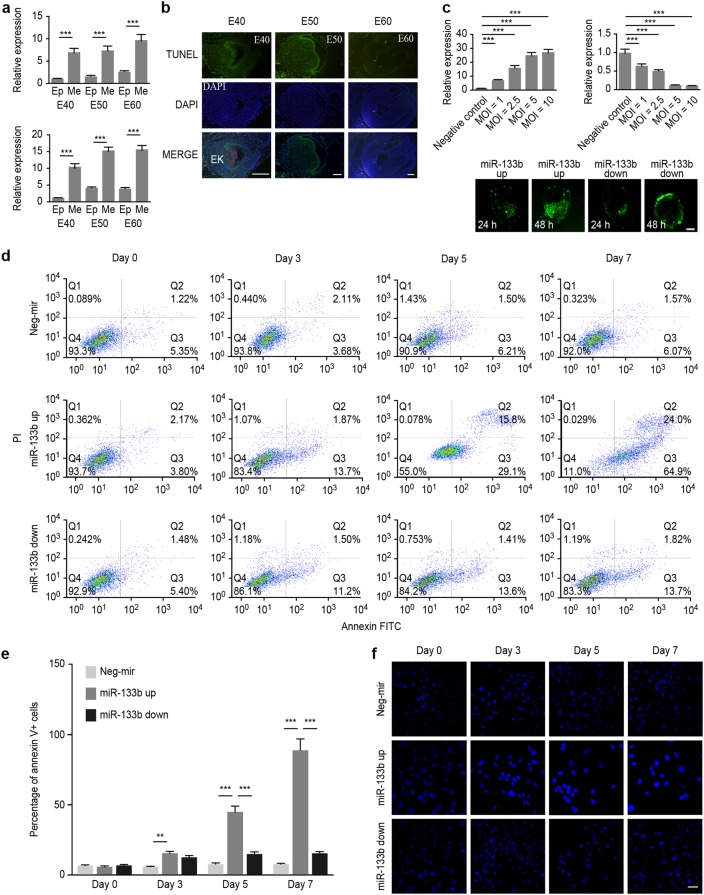
Fig. 1.
Ssc-mir-133b was highly related to cell apoptosis in the early stages of premolar development. a Relative expression of ssc-mir-133b in premolar dental epithelium and mesenchyme using qPCR. U6 was used as a control. Average ssc-mir-133b expression levels in premolar the dental mesenchyme were significantly higher than in the dental epithelium (upper panel). Similarly, the ssc-mir-133b expression levels in primary premolar dental mesenchyme cells were significantly higher than in dental epithelium cells (lower panel). ***P < 0.001. b Apoptosis was measured with a TUNEL assay in E40, E50, and E60 premolars. Scale bar = 200 μm. Enamel knots (EK, red dotted circle). c Relative ssc-mir-133b expression levels at 48 h after transfection of different MOIs of ssc-mir-133b lentiviral vectors and the efficiency of ssc-mir-133b lentiviral vector transfection. Average ssc-mir-133b expression levels after transfection with ssc-mir-133b overexpression lentiviral vector (upper left). average ssc-mir-133b expression levels after transfection with ssc-mir-133b inhibition lentiviral vector (upper right). ***P < 0.001. The efficiency of the ssc-mir-133b lentiviral vector (lower). d Cells dually stained with annexin-FITC/PI were investigated by flow cytometry analysis. Q1 quadrant represents the living cells; Q2 quadrant represents the early apoptotic cells; Q3 quadrant represents the late apoptotic cells; and Q4 quadrant represents the dead cells. e Statistical analysis of flow cytometry results. ***P < 0.001 and **P < 0.01. f Transfected premolar mesenchymal cells were stained with Hoechst 33342 on coverslips. A fluorescence microscope was used to photograph the results. Bar = 50 μm