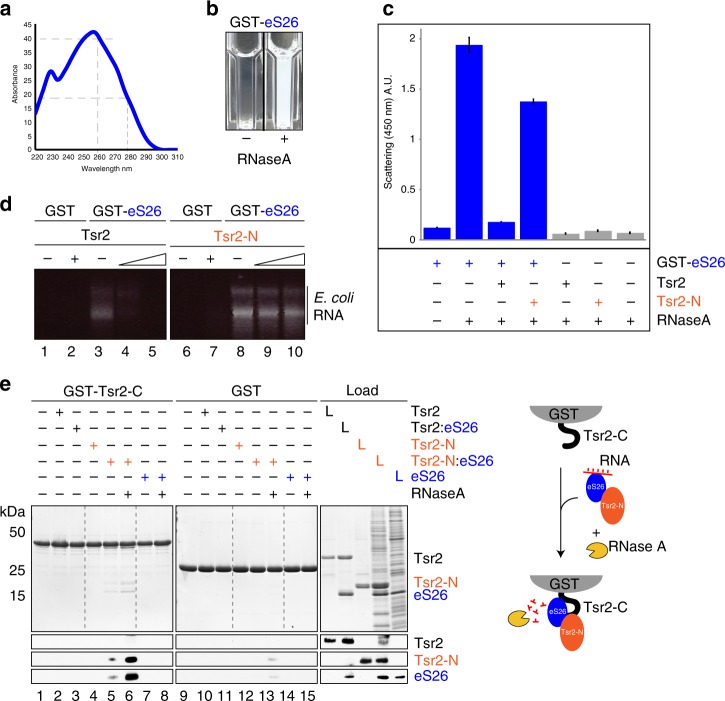
Fig. 6.
C-terminal acidic tail of Tsr2 keeps eS26-RNA free. a eS26 co-enriches nucleic acids. b RNase A triggers aggregation of eS26. GST-eS26 was treated with RNase A and incubated for 10 min at RT in a photometric cuvette. c Tsr2 prevents aggregation of recombinant eS26 in vitro. Thirty-three micromolar GST-eS26 and a two-fold concentration of Tsr2 (66 µM) in PBSKMT was pre-incubated for 1 h at 4 °C (final volume: 90 µl). One microgram of RNase A was added to initiate aggregation. After 1 h of incubation, the scattering signal of the aggregated eS26 was monitored at 450 nm (Y-axes). Three replicates for each well were measured. The error bars show the standard deviation. d Tsr2 releases RNA bound to GST-eS26. RNA was extracted from immobilized GST-eS26 after addition of increasing amounts of Tsr2 or Tsr2-N, respectively, separated on a 1% agarose gel and stained by EtBr. e GST-Tsr2-C was immobilized on Glutathione Sepharose before incubation with purified Tsr2, Tsr2-N or/and an E. coli lysate containing recombinant eS26 in the presence or absence of RNaseA. L = input (1:10 diluted)