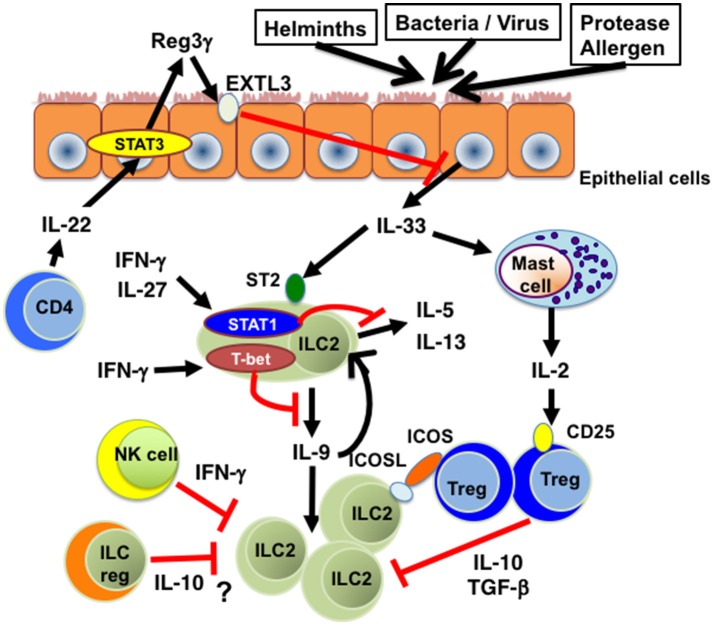
Figure 1.
The inhibitory effects of cytokines on IL-33-ST2-ILC2 axis. Th1 cell-related cytokines such as IFN-γ and IL-27 inhibit IL-33-induced cytokine production and proliferation of ILC2s in a STAT1-dependent manner. T-bet expressed in ILC2s suppresses IL-9 production and subsequent expansion of ILC2s. IL-22 produced by CD4+ T cells suppresses IL-33 production from lung epithelial cells through Reg3γ induction. IL-2 produced by IL-33-stimulated mast cells promotes the expansion of Tregs, which suppress ILC2-mediated inflammation through the production of IL-10 and TGF-β. ICOS-ICOSL-mediated cell contact is also involved in Treg-mediated ILC2 suppression. In addition, IFN-γ produced by NK cells inhibits cytokine production and function of ILC2s. Moreover, IL-10-producing ILCregs could be a suppresser of IL-33-ST2-ILC2-mediated inflammation. EXTL3, exostatin-like 3; ICOS, inducible T-cell costimulator; ICOSL, inducible T-cell costimulator ligand; ILC2, group 2 innate lymphoid cells; ILCreg, regulatory innate lymphoid cell. NK cell, natural killer cell; Reg3γ, regenerating islet-derived protein 3 gamma; STAT1, signal transducer and activator or transcription 1; STAT3, signal transducer and activator or transcription 3; ST2, suppression of tumorigenicity 2; T-bet, T-box transcription factor expressed in T-cells; Treg, regulatory T cell.