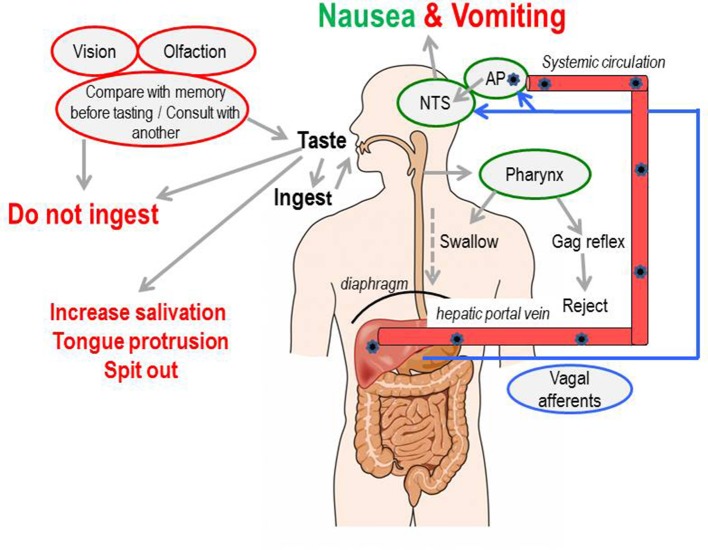
Figure 1.
A summary of the levels of defense employed to initially avoid and, if required, to detect and respond to toxins ingested with the food. AP, area postrema (also known as the “chemoreceptor trigger zone” for emesis, but see text for discussion); NTS, nucleus tractus solitarius; the site in the dorsal brainstem where inputs from the vagal afferents and the area postrema are integrated and from which outputs pass to other areas of the brainstem to coordinate the motor outputs for vomiting and from which information is relayed to “higher” brain regions to evoke the sensation of nausea. Figure adapted and modified from Andrews (1993).