Figure 1.
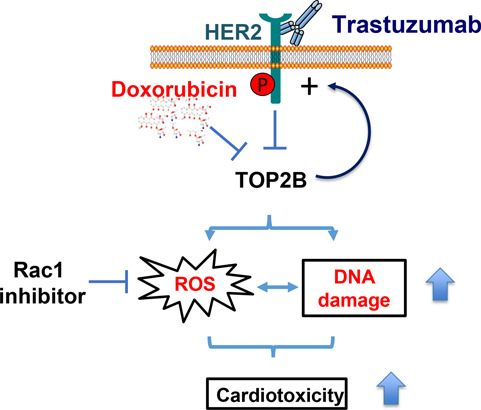
TOP2B: a shared target for the cardiotoxicity induced by doxorubicin and trastuzumab.
Both of doxorubicin and trastuzumab inhibit TOP2B in human cardiomyocytes. Their combined cardiotoxic effect at the cellular level is associated with increased ROS production and DNA damage enhancement. While doxorubicin inhibits TOP2 activity, it also enhances the levels of HER2 expression in human cardiomyocytes, which may render the cardiomyocytes to become addicted to HER2 signaling for survival under stressed conditions, leading to cardiomyocytes becoming more sensitive to trastuzumab treatment after doxorubicin exposure. Our proposed model explains the elevated cardiotoxicity induced by trastuzumab and doxorubicin combination therapy. In addition, Rac1, a small GTPase inhibitor, prevents trastuzumab from inducing DNA damage and suppresses increased ROS production induced by either trastuzumab alone or combination of doxorubicin and trastuzumab, suggesting that Rac1 inhibitor may be used to antagonize cardiotoxicity induced by trastuzumab or trastuzumab and doxorubicin combination therapy.
