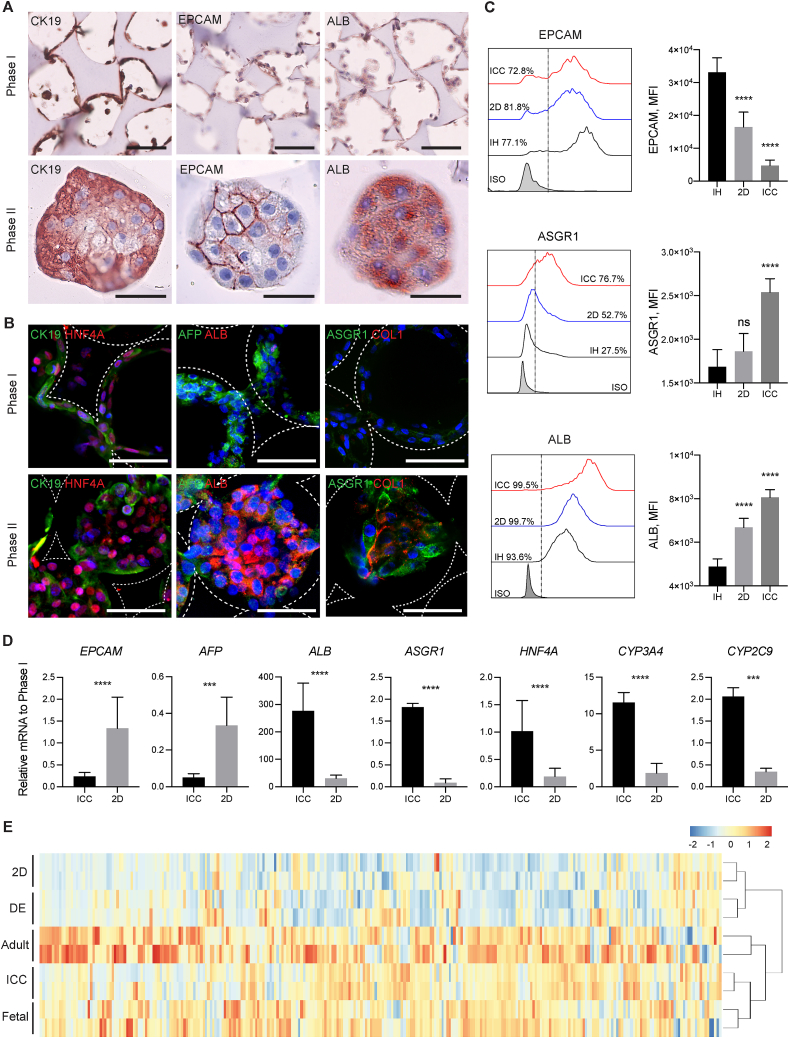
Fig. 3.
Morphological and transcriptomic characterization of IH-ICC organoids. (A) Histochemical images demonstrating morphogenesis of IH from a single cell layer (Phase I top panel; scale bar, 100 μm) to organoids (Phase II bottom panel; scale bar, 50 μm) occurs in conjunction with differential protein expression of developmental markers CK19 (left), EPCAM (middle) and ALB (right). (B) Confocal micrographs highlighting upregulated protein expression of mature (ALB, ASGPR1, COL1) hepatic markers occurs in conjunction with down regulation of immature (CK19 and AFP) markers during transition of IH from Phase I (top panel; scale bar, 100 μm) to Phase II (bottom panel; scale bar, 100 μm) organoids. (C) FACS histogram and mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) analysis demonstrating hepatic maturation kinetics of IH in ICC vs 2D culture (N = 4). (D) Differential gene expression (by RT-PCR) of selected genes reveals a more mature hepatic signature of IH in ICC vs. 2D culture (N = 8). (e) Bi-clustering heatmap of 296 liver-specific genes across different primary (adult & fetal liver) and IH (DE, 2D & ICC) samples. Samples are linked by the dendrogram above to show the similarity of their gene expression patterns. Mean ± sd, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.0005; ****p < 0.0001; ns nonsignificant.