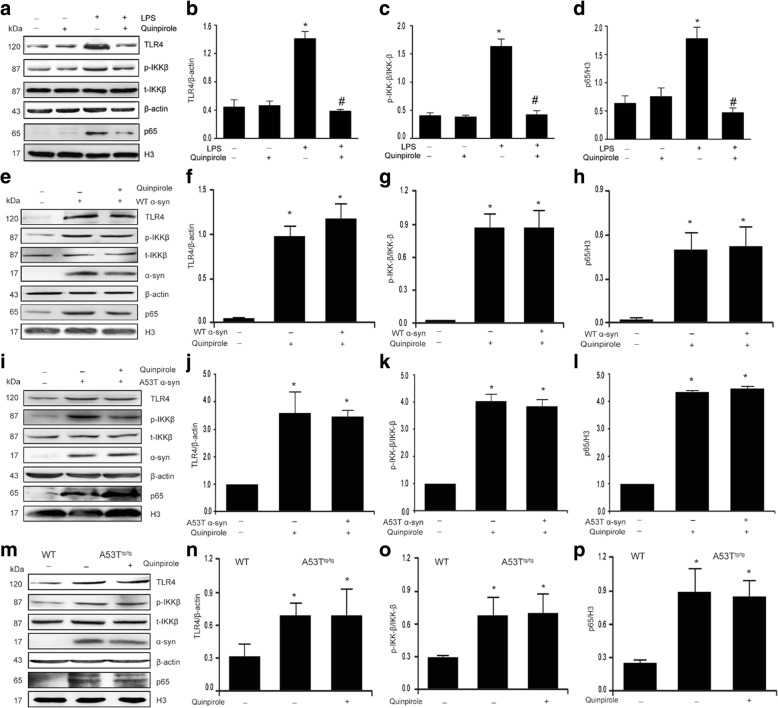
Fig. 4.
α-Synuclein abolishes Drd2-mediated inhibition of TLR4-NF-κB signaling in astrocytes. a–d Quinpirole inhibited the LPS-induced activation of TLR4-NF-κB signaling in astrocytes. Representative immunoblot (a) and quantitative analysis of TLR4 (b), p-IKK (c), and nuclear p65 (d) in astrocytes treated with LPS and quinpirole. e–h Quinpirole failed to suppress the activation of TLR4-NF-κB signaling induced by wide-type (WT) α-Syn. Representative immunoblot (e) and quantitative analysis of TLR4 (f), p-IKK (g), and nuclear p65 (h) in astrocytes treated with WT α-Syn and quinpirole. i–l Quinpirole failed to suppress the activation of TLR4-NF-κB signaling induced by A53T mutant α-Syn. Representative immunoblot (i) and quantitative analysis of TLR4 (j), p-IKK (k), and nuclear p65 (l) in astrocytes treated with A53T\α-Syn and quinpirole. m–p Quinpirole failed to suppress the activation of TLR4-NF-κB signaling in astrocytes of A53T transgenic (A53Ttg/tg) mice. Representative immunoblot (m) and quantitative analysis of TLR4 (n), p-IKK (o), and nuclear p65 (p) in astrocytes of A53Ttg/tg mice treated with quinpirole. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M from four independent experiments, one-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05 vs. control group, and #p < 0.05 vs. LPS treatment group